Page 19 - E-LKM ASAM BASA
P. 19
The Effect of subsituens on
the strength of acid and base
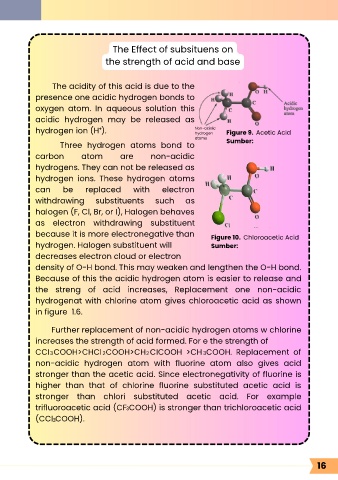
The acidity of this acid is due to the
presence one acidic hydrogen bonds to
oxygen atom. In aqueous solution this
acidic hydrogen may be released as
+
hydrogen ion (H ). Non-acidic Figure 9. Acetic Acid
hydrogen
atoms Sumber:
Three hydrogen atoms bond to
carbon atom are non-acidic
hydrogens. They can not be released as
hydrogen ions. These hydrogen atoms
can be replaced with electron
withdrawing substituents such as
halogen (F, Cl, Br, or I), Halogen behaves
as electron withdrawing substituent
because it is more electronegative than Figure 10. Chloroacetic Acid
hydrogen. Halogen substituent will Sumber:
decreases electron cloud or electron
density of O-H bond. This may weaken and lengthen the O-H bond.
Because of this the acidic hydrogen atom is easier to release and
the streng of acid increases, Replacement one non-acidic
hydrogenat with chlorine atom gives chloroacetic acid as shown
in figure 1.6.
Further replacement of non-acidic hydrogen atoms w chlorine
increases the strength of acid formed. For e the strength of
CCI COOH>CHCl COOH>CH CICOOH >CH COOH. Replacement of
2
3
2
3
non-acidic hydrogen atom with fluorine atom also gives acid
stronger than the acetic acid. Since electronegativity of fluorine is
higher than that of chlorine fluorine substituted acetic acid is
stronger than chlori substituted acetic acid. For example
trifluoroacetic acid (CF COOH) is stronger than trichloroacetic acid
3
(CCI COOH).
3
16