Page 67 - 台灣肝癌醫學冬季會手冊-1222-V3_Neat
P. 67
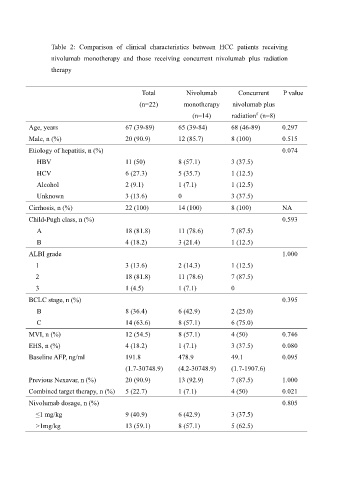
Table 2: Comparison of clinical characteristics between HCC patients receiving
nivolumab monotherapy and those receiving concurrent nivolumab plus radiation
therapy
Total Nivolumab Concurrent P value
(n=22) monotherapy nivolumab plus
#
(n=14) radiation (n=8)
Age, years 67 (39-89) 65 (39-84) 68 (46-89) 0.297
Male, n (%) 20 (90.9) 12 (85.7) 8 (100) 0.515
Etiology of hepatitis, n (%) 0.074
HBV 11 (50) 8 (57.1) 3 (37.5)
HCV 6 (27.3) 5 (35.7) 1 (12.5)
Alcohol 2 (9.1) 1 (7.1) 1 (12.5)
Unknown 3 (13.6) 0 3 (37.5)
Cirrhosis, n (%) 22 (100) 14 (100) 8 (100) NA
Child-Pugh class, n (%) 0.593
A 18 (81.8) 11 (78.6) 7 (87.5)
B 4 (18.2) 3 (21.4) 1 (12.5)
ALBI grade 1.000
1 3 (13.6) 2 (14.3) 1 (12.5)
2 18 (81.8) 11 (78.6) 7 (87.5)
3 1 (4.5) 1 (7.1) 0
BCLC stage, n (%) 0.395
B 8 (36.4) 6 (42.9) 2 (25.0)
C 14 (63.6) 8 (57.1) 6 (75.0)
MVI, n (%) 12 (54.5) 8 (57.1) 4 (50) 0.746
EHS, n (%) 4 (18.2) 1 (7.1) 3 (37.5) 0.080
Baseline AFP, ng/ml 191.8 478.9 49.1 0.095
(1.7-30748.9) (4.2-30748.9) (1.7-1907.6)
Previous Nexavar, n (%) 20 (90.9) 13 (92.9) 7 (87.5) 1.000
Combined target therapy, n (%) 5 (22.7) 1 (7.1) 4 (50) 0.021
Nivolumab dosage, n (%) 0.805
≤1 mg/kg 9 (40.9) 6 (42.9) 3 (37.5)
>1mg/kg 13 (59.1) 8 (57.1) 5 (62.5)