Page 5 - DIFDUF
P. 5
723
form was independently reviewed by two physicians (who were
electronic forms by trained research nurses. Subsequently, each
manually recorded. Data were abstracted and summarized into
nursing notes. For each record, the total medication dose was
progress and consultation notes, discharge summaries, and
medication lists, laboratory reports, admission histories,
triggers and potential ADEs. We reviewed physician orders,
charts were initially reviewed by a research nurse to identify
ing changes were reached only by consensus. Hospitalization
and discussed the need for trigger adaptation. Decisions regard-
tion, all listed researchers reviewed the various ADE triggers
the methodology as set by the IHI [10]. Prior to the study initia-
ADE identification and characterization was conducted using
CHART REVIEw fOR ADVERSE DRug EVEnTS
institutional review board at each of the participating hospitals.
Corp, Richmond, CA, USA). The study was approved by the
Microsoft Excel (version 14.0.6212.5000) software (Microsoft
hospitalizations to be included in the study sample using
the inclusion criteria were included. We then randomly selected
stay between 2 days and 1 month. All hospitalizations that met
hospitalized patients 18 years of age or older with a hospital
2014 at each of the four hospitals studied. Inclusion criteria were
cine and surgical departments between January and December
comprised patients who had been hospitalized in internal medi-
the other three having a partial system. The study population
chart usage, with one having a full system including CPOE and
pitals had different levels of sophistication in electronic medical
medical centers varying in size from 326 to 1517 beds. The hos-
geographical regions. All four hospitals are public academic
surveying four general hospitals in Israel located in different
The study was a retrospective descriptive correlative analysis
STuDy pOpulATIOn AnD SETTIng
PATIENTS AND METHODS
in Israel and to define the ADE rates in four different hospitals.
objective of the present study was to validate the Trigger Tool
of 25% and 32% in 1997 and 1998, respectively [20,21]. The
In Israel, the evidence is scant with estimated ADE rates
was not adopted in British hospitals.
mated 40% sensitivity for preventable ADEs, the Trigger Tool
the relatively low PPV in the British study, along with an esti-
In Israel, the medical field is seeing the first signs of activity
prevalence of 3.4% in Britain and 15.6% in Brazil [17,19]. Given
[16,17]. This finding is further reflected by variance in ADE
between 4.0% and 21.5% in Britain and Belgium, respectively
predictive value (PPV). The latter has been reported to range
were shown to affect the Trigger Tool sensitivity and its positive
However, between-country differences in medical practices
more ADEs in approximately one-third of all hospitalizations.
the Trigger Tool was shown to assist in identifying 10 times
Furthermore, compared to other ADE reporting systems,
ConferenCe preCedings ConferenCe preCedings saying, “In what may be called the natural method of teaching, William Osler addressed the New York Academy of Medicine participate in the teaching process started in 1903, when Sir professional work (publication in process). Having the patient field and 81% felt that the program contributes to their daily program was of added value to practitioners in the diabetes ing were conducted. All participants noted that t
#
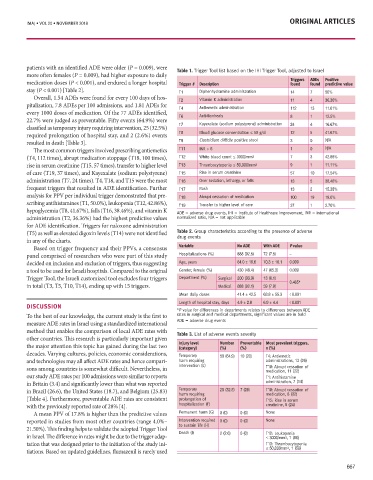
patient Involvement in the Design and policy in patients with an identified ADE were older (P = 0.009), were Table 1. Trigger Tool list based on the IHI Trigger Tool, adjusted to Israel
Healthcare: Highlights from the 4th Annual Conference more often females (P = 0.009), had higher exposure to daily Trigger # Description Triggers ADEs positive
medication doses (P < 0.001), and endured a longer hospital
predictive value
found
found
on Therapeutic patient Education in Diabetes OTzMA, stay (P < 0.001) [Table 2]. T1 Diphenhydramine administration 14 7 4 50%
Overall, 1.54 ADEs were found for every 100 days of hos-
Vitamin K administration
36.36%
T2
11
pitalization, 7.8 ADEs per 100 admissions, and 1.81 ADEs for Antiemetic administration
21 March 2018 every 1000 doses of medication. Of the 77 ADEs identified, T4 Antidiarrheals 112 13 11.61%
22.7% were judged as preventable. Fifty events (64.9%) were T6 8 1 12.5%
Vardit M. Kalamaro PharmD , Karen Harshkop RN PhD , Rose Lipner and Orly Tamir MHA MSc PhD 1 classified as temporary injury requiring intervention, 25 (32.5%) T7 Kayexalate (sodium polystyrene) administration 24 4 16.67%
1
1
2
required prolongation of hospital stay, and 2 (2.6%) events T8 Blood glucose concentration ≤ 50 g/dl 12 5 41.67%
1 Israeli Center for Research and Policy in Diabetes, Gertner Institute for Epidemiology and Health Policy Research, Sheba Medical Center, Tel Hashomer, Israel resulted in death [Table 3]. T9 Clostridium difficile positive stool 3 0 N/A
2 Department of Nutrition and Dietetics, New York University, New York, New York, USA
The most common triggers involved prescribing antiemetics T11 INR > 6 1 0 N/A
131118-COHANIM - 131118-COHANIM | 1 - A | 18-11-13 | 11:24:13 | SR:-- | Magenta
(T4, 112 times), abrupt medication stoppage (T18, 100 times), T12 White blood count ≤ 3000/mm 3 7 3 42.86%
131118-COHANIM - 131118-COHANIM | 1 - A | 18-11-13 | 11:24:13 | SR:-- | Yellow
#131118-COHANIM - 131118-COHANIM | 1 - A | 18-11-13 | 11:24:13 | SR:-- | Black
rise in serum creatinine (T15, 57 times), transfer to higher level T13 Thrombocytopenia ≤ 50,000/mm 3 9 1 11.11%
131118-COHANIM - 131118-COHANIM | 1 - A | 18-11-13 | 11:24:13 | SR:-- | Cyan
of care (T19, 37 times), and Kayexalate (sodium polystyrene) T15 Rise in serum creatinine 57 10 17.54%
economic burden [3,4]. Karasik emphasized that the process administration (T7, 24 times). T4, T18, and T15 were the most T16 Over sedation, lethargy, or falls 13 5 38.46%
KEY WORDS: 4th Annual Conference on Therapeutic Patient Education in of implementing patient involvement within the Israeli health- frequent triggers that resulted in ADE identification. Further T17 Rash 13 2 15.38%
Diabetes, diabetes education program, healthcare policy, care system is slow and that the time has come to adapt and analysis for PPV per individual trigger demonstrated that pre- T18 Abrupt cessation of medication 100 19 19.0%
patient advocacy, patient involvement learn from other countries that have already integrated patient scribing antihistamines (T1, 50.0%), leukopenia (T12, 42.86%), T19 Transfer to higher level of care 37 1 2.70%
IMAJ 2018; 20: 722–724 involvement within their national health system [3-5]. hypoglycemia (T8, 41.67%), falls (T16, 38.46%), and vitamin K ADE = adverse drug events, IHI = Institute of Healthcare improvement, INR = international
England is an example of a country that has instituted administration (T2, 36.36%) had the highest predictive values normalized ratio, N/A = not applicable
patient involvement within health policy initiatives. In April for ADE identification. Triggers for naloxone administration
2017, the United Kingdom National Health System (NHS), (T5) as well as elevated digoxin levels (T14) were not identified Table 2. Group characteristics according to the presence of adverse
published an official updated version of their Patient and Public in any of the charts. drug events
he 4th Annual Conference on Therapeutic Patient Edu- Participation Policy, which was designed to strengthen patient Based on trigger frequency and their PPVs, a consensus Variable No ADE With ADE P value
T cation in Diabetes was held at the Daniel Hotel in Herzliya, and public interest in the NHS [3]. The British health system panel comprised of researchers who were part of this study Hospitalizations (%) 888 (92.5) 72 (7.5) –
Israel, on 21 March 2018. The focus of the conference was to recognizes patients and the public. This group includes every- decided on inclusion and exclusion of triggers, thus suggesting Age, years 64.0 ± 19.6 70.3 ± 16.1 0.009
raise awareness of the expanding trend of patient involvement one who uses services, who may do so in the future, or who is a tool to be used for Israeli hospitals. Compared to the original Gender, female (%) 430 (48.4) 47 (65.3) 0.009
in the design and policy in healthcare [1]. strengthening their participation in various aspects of making Trigger Tool, the Israeli customized tool excludes four triggers Department (%) Surgical 200 (93.9) 13 (6.1)
Over the last 2 decades healthcare has gone from a patri- health policy. in total (T3, T5, T10, T14), ending up with 15 triggers. Medical 688 (92.1) 59 (7.9) 0.465*
archal conception, in which the healthcare provider dictates The patients and public are involved at all levels, including Mean daily doses 41.4 ± 42.5 63.8 ± 55.3 < 0.001
treatment approaches to disease, to a more patient-centered commissioning processes and decisions like planning, buying, Length of hospital stay, days 4.9 ± 2.8 6.9 ± 4.4 < 0.001
approach in which there is a partnership between the patient and monitoring services. They are also involved in the ongo- DISCUSSION *P value for differences in departments relates to differences between ADE
and healthcare provider in determining a treatment plan. As a ing work of various committees and working groups related to To the best of our knowledge, the current study is the first to rates in surgical and medical departments, significant values are in bold
result, patients and their families are becoming more involved health policy and research in health. measure ADE rates in Israel using a standardized international ADE = adverse drug events
and active also within the policy-making processes in health- method that enables the comparison of local ADE rates with Table 3. List of adverse events severity
care systems [2]. pATIEnT InVOlVEMEnT: BMJ pATIEnT pARTnERSHIp pROgRAM other countries. This research is particularly important given
The conference was organized by the OTZMA Diabetes Dr. Tessa Richards, senior editor at the British Medical Journal the major attention this topic has gained during the last two Injury level Number Preventable Most prevalent triggers,
(%)
n (%)
(category)
(%)
Care Initiative. Clinicians, healthcare providers, and patients (BMJ) and leader of the BMJ patient partnership initiative, decades. Varying cultures, policies, economic considerations, Temporary 50 (64.9) 10 (20) T4: Antiemetic
from transverse health systems attended the conference, which presented the BMJ patient partnership program, which began and technologies may all affect ADE rates and hence compari- harm requiring administrations, 13 (26)
focused on patient involvement in various processes within about 4 years earlier with the implementation of an innovative sons among countries is somewhat difficult. Nevertheless, in intervention (E) T18: Abrupt cessation of
medication, 11 (22)
the healthcare system. Participants presented specific activi- strategy called “Walking the Talk” [6]. Within the program, an our study ADE rates per 100 admissions were similar to reports T1: Antihistamine
ties regarding the design of services and policy changes, which international patient advisory panel was established to develop in Britain (3.4) and significantly lower than what was reported administration, 7 (14)
occur in other countries or in Israel. a plan to promote patient partnership. The BMJ aspired to in Brazil (26.6), the United States (18.7), and Belgium (25.83) Temporary 25 (32.5) 7 (28) T18: Abrupt cessation of
medication, 8 (32)
harm requiring
advance a change in healthcare systems. Richards discussed [Table 4]. Furthermore, preventable ADE rates are consistent prolongation of T15: Rise in serum
pATIEnT InVOlVEMEnT: RESEARCH AnD THE HEAlTHCARE SySTEM the reasons for this move and how the strategy was developed with the previously reported rate of 28% [4]. hospitalization (F) creatinine, 6 (24)
Chairman of the conference, Prof. Avi Karasik, president of the including its evolution and attempts to spread this initiative A mean PPV of 17.8% is higher than the predictive values Permanent harm (G) 0 (0) 0 (0) None
Israel Endocrine Society, highlighted the importance of more across the 70 journals of the BMJ group and beyond. For reported in studies from most other countries (range 4.0%– Intervention required 0 (0) 0 (0) None
to sustain life (H)
example, authors of research papers have been asked to state
21.50%). This finding helps to validate the adopted Trigger Tool
patient involvement in research and the healthcare system,
PERFECTOR recognizing that presenting the service to the recipients, who whether and how they involved patients when choosing their in Israel. The difference in rates might be due to the trigger adap- ≤ 3000/mm 3 , 1 (50)
Death (I)
0 (0)
2 (2.6)
T12: Leukopenia
are patients and their families, at the planning stage will lead to
tation that was designed prior to the initiation of the study ini-
research questions, study designs, and outcome measures, as
T13: Thrombocytopenia
≤ 50,000mm 3 , 1 (50)
tiations. Based on updated guidelines, flumazenil is rarely used
better patient services and health outcomes and will lower the
well as how they implemented and disseminated study results.
722 667