Page 6 - DIFDUF
P. 6
665
*The first and second authors contributed equally to this study
KEY WORDS:
ABSTRACT:
131118-COHANIM - 131118-COHANIM | 1 - B | 18-11-13 | 11:24:13 | SR:-- | Cyan
#131118-COHANIM - 131118-COHANIM | 1 - B | 18-11-13 | 11:24:13 | SR:-- | Black
131118-COHANIM - 131118-COHANIM | 1 - B | 18-11-13 | 11:24:13 | SR:-- | Yellow
131118-COHANIM - 131118-COHANIM | 1 - B | 18-11-13 | 11:24:13 | SR:-- | Magenta
3
#
Original articles Original articles 1,7 1,7 dverse drug events (ADEs) are a major cause of morbidity Aside from prevention, identifying an ADE is crucial for The process of in-hospital drug administration is a multi- United States as well as in various European countries [11-18]. requirements enabled its introduction in many hospitals in the process that might reveal an ADE. Its low cost and rapid training procedure is followed by tracking the trig
A hypertensive 89 year old woman After 9 days, the transcathteter closure of the septum; however, in case of hemo-
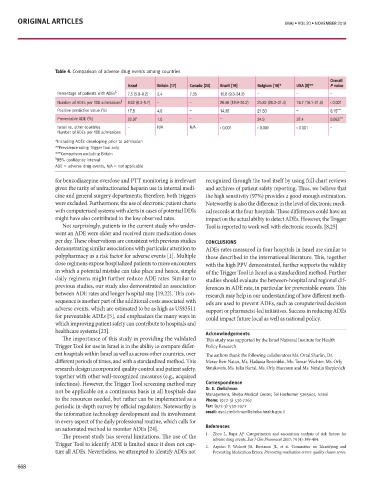
Table 4. Comparison of adverse drug events among countries
was admitted to our institution 72 hours of this VSD was performed with a 20 mm dynamic instability, this timing may not be
Overall after complaining of chest pain. The elec- Amplatzer TM Post-MI VSD Occluder (St. observed. Treatment with aspirin alone for
Israel Britain [17] Canada [24] Brazil [19] Belgium [16]* uSA [8]** p value
Percentage of patients with ADEs § 7.5 (5.8–9.2) 3.4 7.35 15.6 (9.3–34.2) – – – trocardiogram (ECG) showed an inferior Jude Medical, USA) [Figure 1E]. Figure 1D 6 months seems to be proper treatment. In
shows the steps of the transcatheter VSD
cases of persistent significant shunt, anti-
ST-elevation myocardial infarct (STEMI).
Number of ADEs per 100 admissions § 8.02 (6.3–9.7) – – 26.56 (18.9–34.2) 25.83 (20.3–31.4) 18.7 (16.1–21.5) < 0.001 Clinical examination revealed sinus tachy- closure with the insertion of the closure platelet therapy would not increase success.
Positive predictive value (%) 17.8 4.0 – 14.35 21.50 – 0.15 *** cardia, normal blood pressure, and holo- device using a transeptal access via the However, progress in the field of percutane-
Preventable ADE (%) 22.07 1.0 – – 34.9 37.4 0.053 *** systolic murmur on the precordium graded transfemoral venous route. The defect was ous interventions and mechanical support
Israel vs. other countries – N/A N/A < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 – 4/6 with jugular venous distension. Urgent crossed using a balloon tip catheter, and could improve the outcomes of this kind of
Number of ADEs per 100 admissions
TTE showed a left ventricle ejection frac- an Amplatz Super Stiff TM ST-1 guidewire rare and severe complication.
*Including ADEs developing prior to admission tion of 45% with inferoseptal and inferior (Boston Scientific, USA) was subsequently
**Prevalence using Trigger tool only akinesia as well as the presence of a large positioned in the right pulmonary artery Correspondence
***Comparison excluding Britain Dr. f. Rey
§ 95% confidence interval VSD with left-to-right shunt highlighted to advance the 12F delivery system. A mild Dept. of Medicine, Montreal Heart Institute,
ADE = adverse drug events, N/A = not applicable on the color Doppler [Figure 1A, 1B]. residual leak was seen on post-procedural Montreal QC H1T 1C8, Canada
Coronary angiogram revealed a sub- TTE [Figure 1F, 1G]. The patient was treated email: reyflor5@gmail.com
for benzodiazepine overdose and PTT monitoring is irrelevant recognized through the tool itself by using full chart reviews occlusion of the posterior descending, with aspirin and clopidogrel.
given the rarity of unfractionated heparin use in internal medi- and archives of patient safety reporting. Thus, we believe that and retroventricular arteries were treated It is important to note that in the acute References
cine and general surgery departments; therefore, both triggers the high sensitivity (97%) provides a good enough estimation. by two drug eluting stents due to ongoing setting, the closure of the VSD decreased 1. Levi Y, Frimerman A, Shotan A, et al. Primary
were excluded. Furthermore, the use of electronic patient charts Noteworthy is also the difference in the level of electronic medi- ischemia. Right heart catheterization con- the shunt but it did not eliminate it com- percutaneous coronary intervention versus in-
hospital thrombolysis as reperfusion therapy in
with computerized systems with alerts in cases of potential DDIs cal records at the four hospitals. These differences could have an firmed an important left-to-right shunt and pletely. Maintenance of the IABP at least 48 early-arriving low-risk STEMI patients. IMAJ 2017;
might have also contributed to the low observed rates. impact on the actual ability to detect ADEs. However, the Trigger low cardiac output. The left ventriculogram hours or more, depending on the hemody- 19 (6): 345-50.
Not surprisingly, patients in the current study who under- Tool is reported to work well with electronic records. [8,25] showed a VSD with sufficient distance from namic repercussion, should be considered. 2. Karkabi B, Jaffe R, Halon DA, et al. An intervention
went an ADE were older and received more medication doses the apex and a 14 mm defect size [Figure Unfortunately, in our case, 1 day after the to reduce the time interval between hospital entry
and emergency coronary angiography in patients
per day. These observations are consistent with previous studies COnCluSIOnS 1C]. An IABP was inserted. insertion of the IABP, the patient still could with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. IMAJ 2017;
demonstrating similar associations with particular attention to ADEs rates measured in four hospitals in Israel are similar to The subsequent modality of closure, not be weaned and the patient requested a 19 (9): 547-52.
polypharmacy as a risk factor for adverse events [1]. Multiple those described in the international literature. This, together either surgical or transcatheter, as well therapeutic withdrawal. 3. Jones BM, Kapadia SR, Smedira NG, et al.
Ventricular septal rupture complicating acute
dose regimens expose hospitalized patients to more encounters with the high PPV demonstrated, further supports the validity as the ideal timing, was discussed in the Although 30 years have passed since the myocardial infarction: a contemporary review. Eur
in which a potential mistake can take place and hence, simple of the Trigger Tool in Israel as a standardized method. Further heart team. Past research has suggested a first transcatheter closure, the best timing Heart J 2014; 35: 2060-8.
daily regimens might further reduce ADE rates. Similar to studies should evaluate the between-hospital and regional dif- post-MI VSD closure at least 7–10 days or of post-MI VSD closure and the regimen 4. Schlotter F, de Waha S, Eitel I, et al. Interventional
post-myocardial infarction ventricular septal defect
previous studies, our study also demonstrated an association ferences in ADE rate, in particular for preventable events. This later after the STEMI because of the risk of antiplatelet therapy after the closure closure: a systematic review of current evidence.
between ADE rates and longer hospital stay [19,22]. This con- research may help in our understanding of how different meth- of a crumbly septum muscular wall in the remains uncertain [5]. Surgical or trans- Eurointervention 2016; 12: 94-102.
sequence is another part of the additional costs associated with ods are used to prevent ADEs, such as computerized decision acute setting. Successful closure decreases catheter closure after 7 to 10 days could ide- 5. Lock JE, Block PC, McKay RG, et al. Transcatheter
closure of ventricular septal defects. Circulation
adverse events, which are estimated to be as high as US$3511 support or pharmacist-led initiatives. Success in reducing ADEs the 30 day mortality rate to 30–40% [3,4]. ally be the best timing due to the weakness 1988; 78: 361-8.
for preventable ADEs [5], and emphasizes the many ways in could impact future local as well as national policy.
which improving patient safety can contribute to hospitals and Capsule
healthcare systems [23]. Acknowledgements
The importance of this study in providing the validated This study was supported by the Israel National Institute for Health The genetic basis and cell of origin of mixed phenotype acute leukaemia
Trigger Tool for use in Israel is in the ability to compare differ- Policy Research
ent hospitals within Israel as well as across other countries, over The authors thank the following collaborators Ms. Ortal Sharlin, Dr. Mixed phenotype acute leukaemia (MPAL) is a high-risk subtype variation, that founding lesions arise in primitive haematopoietic
different periods of times, and with a standardized method. This Merav Ben-Natan, Ms. Hadassa Rosenblat, Ms. Tamar Wechter, Ms. Orly of leukaemia with myeloid and lymphoid features, limited progenitors, and that individual phenotypic subpopulations can
research design incorporated quality control and patient safety, Statskovits, Ms. Julia Bartal, Ms. Orly Haccoun and Ms. Natalia Sheplevich genetic characterization, and a lack of consensus regarding reconstitute the immunophenotypic diversity in vivo. These
together with other well-recognized measures (e.g., acquired appropriate therapy. Alexander and colleagues showed that the findings indicate that the cell of origin and founding lesions,
infections). However, the Trigger Tool screening method may Correspondence two principal subtypes of MPAL, T/myeloid (T/M) and B/myeloid rather than an accumulation of distinct genomic alterations,
are prime tumor cells for lineage promiscuity. Moreover, these
(B/M), are genetically distinct. Rearrangement of ZNF384 is
not be applicable on a continuous basis in all hospitals due Dr. E. zimlichman common in B/M MPAL, and biallelic WT1 alterations are common findings position MPAL in the spectrum of immature leukaemias
Management, Sheba Medical Center, Tel Hashomer 5265601, Israel
to the resources needed, but rather can be implemented as a phone: (972-3) 530-7267 in T/M MPAL, which shares genomic features with early T-cell and provide a genetically informed framework for future clinical
periodic in-depth survey by official regulators. Noteworthy is fax: (972-3) 530-7071 precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. The authors showed trials of potential treatments for MPAL.
the information technology development and its involvement email: eyal.zimlichman@sheba.health.gov.il that the intratumoral immunophenotypic heterogeneity Nature 2018; 562: 373
in every aspect of the daily professional routine, which calls for characteristic of MPAL is independent of somatic genetic Eitan Israeli
an automated method to monitor ADEs [24]. References
The present study has several limitations. The use of the 1. Zhou L, Rupa AP. Categorization and association analysis of risk factors for
adverse drug events. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2017; 74 (4): 389-404.
Trigger Tool to identify ADE is limited since it does not cap- 2. Aspden P, Wolcott JA, Bootman JL, et al. Committee on Identifying and “If life had a second edition, how I would correct the proofs”
ture all ADEs. Nevertheless, we attempted to identify ADEs not Preventing Medication Errors. Preventing medication errors: quality chasm series. John Clare, (1793–1864), English poet
668 721