Page 5 - Straive eBook: Redefining Your Peer Review Experience
P. 5
Straive | Redefining Your Peer Review Experience 5
The Purpose of Peer Review
Peer review in its modern form is a feature of the post-Second World War scholarly
communication landscape (Moxham & Fyfe, 2018). It is seen as an essential part of the
publication process, providing an imprimatur of quality upon which researchers can build their
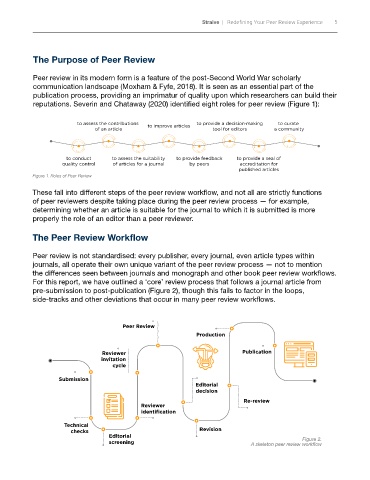
reputations. Severin and Chataway (2020) identified eight roles for peer review (Figure 1):
to assess the contributions to improve articles to provide a decision making to curate
of an article tool for editors a community
to conduct to assess the suitability to provide feedback to provide a seal of
quality control of articles for a journal by peers accreditation for
published articles
Figure 1. Roles of Peer Review
These fall into different steps of the peer review workflow, and not all are strictly functions
of peer reviewers despite taking place during the peer review process — for example,
determining whether an article is suitable for the journal to which it is submitted is more
properly the role of an editor than a peer reviewer.
The Peer Review Workflow
Peer review is not standardised: every publisher, every journal, even article types within
journals, all operate their own unique variant of the peer review process — not to mention
the differences seen between journals and monograph and other book peer review workflows.
For this report, we have outlined a ‘core’ review process that follows a journal article from
pre-submission to post-publication (Figure 2), though this fails to factor in the loops,
side-tracks and other deviations that occur in many peer review workflows.
Peer Review
Production
Reviewer Publication
invitation
cycle
Submission
Editorial
decision
Re-review
Reviewer
identification
Technical
checks Revision
Editorial
Figure 2.
screening A skeleton peer review workflow