Page 212 - Thailand Post Annual Report 2024
P. 212
Part 1
Overview of the Organization
26.3 Credit Risks
Part 2
Business Trends
Part 3
Business Model
Part 4
Strategies and Resource Allocation
Part 5
Risk
Part 6
Corporate Governance
Part 7
Operating Results
Part 8
Other Information
Credit risks are the risks that customers or counterparties are unable to repay to the Group according to the agreed terms upon maturity.
The management has formulated a credit policy to control credit risks on a regular basis by analyzing the financial positions of customers who have applied for a certain level of credit line. As at the report date, no material credit risks were found. The maximum credit risk is expressed in the book value of each financial asset in the statements of financial position. Nevertheless, the management does not anticipate material damage from the inability to collect debts.
26.4 Liquidity Risks
The Group controls the risk of illiquidity by maintaining sufficient levels of cash and cash equivalents for the Group's operations and to mitigate the impact of fluctuations in cash flows.
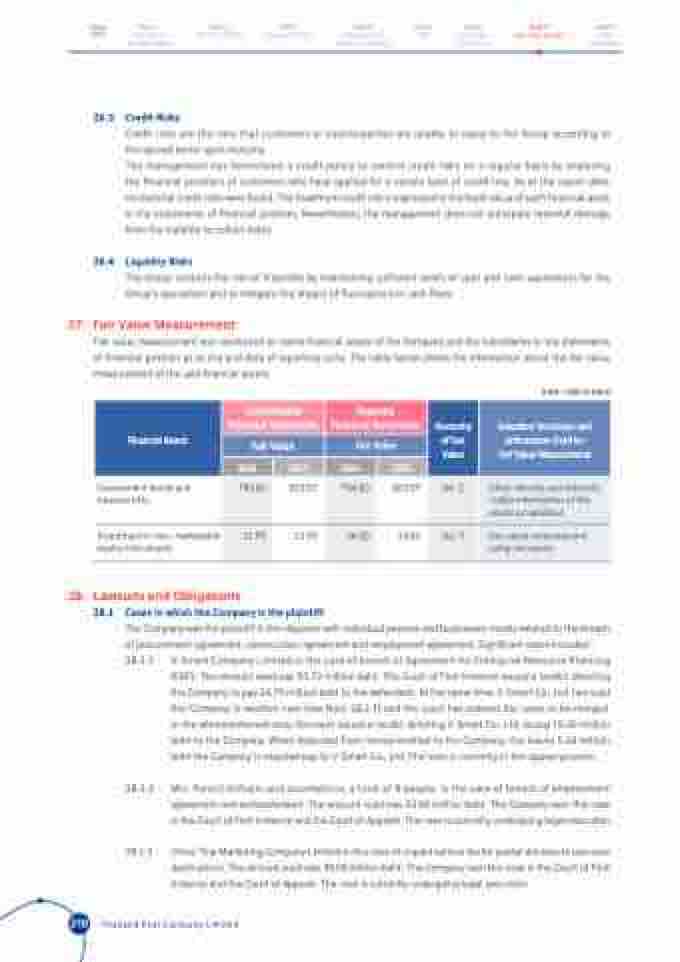
27. Fair Value Measurement
Fair value measurement was conducted on some financial assets of the Company and the subsidiaries in the statements of financial position as at the end date of reporting cycle. The table below shows the information about the fair value measurement of the said financial assets.
(Unit : million baht)
Financial Assets
Consolidated Financial Statements
Separate Financial Statements
Hierarchy of Fair Value
Valuation Technique and Information Used for Fair Value Measurement
Fair Value
Fair Value
2024
2023
2024
2023
Government bonds and treasury bills
754.60
603.57
754.60
603.57
No.2
Other directly and indirectly visible information of the assets or liabilities
Investment in non- marketable equity instruments
21.93
21.93
24.50
24.50
No.3
Fair value measurement using net assets
28. Lawsuits and Obligations
28.1 Cases in which the Company is the plaintiff
The Company was the plaintiff in the disputes with individual persons and businesses mostly related to the breach of procurement agreement, construction agreement and employment agreement. Significant cases included :
28.1.1 V-Smart Company Limited in the case of breach of Agreement for Enterprise Resource Planning
(ERP). The amount sued was 55.72 million baht. The Court of First Instance issued a verdict directing the Company to pay 24.70 million baht to the defendant. At the same time, V-Smart Co., Ltd. has sued the Company in another case (see Note 28.2.1) and the court has ordered the cases to be merged. In the aforementioned case, the court issued a verdict directing V-Smart Co., Ltd. to pay 19.36 million baht to the Company. When deducted from money entitled to the Company, this leaves 5.34 million baht the Company is required pay to V-Smart Co., Ltd. The case is currently in the appeal process.
28.1.2 Mrs. Pensiri Atthajin and accomplices, a total of 8 people, in the case of breach of employment agreement and embezzlement. The amount sued was 53.96 million baht. The Company won this case in the Court of First Instance and the Court of Appeals. The case is currently undergoing legal execution
28.1.3 China Thai Marketing Company Limited in the case of unpaid service fee for postal delivery to overseas destinations. The amount sued was 38.08 million baht. The Company won this case in the Court of First Instance and the Court of Appeals. The case is currently undergoing legal execution
210 Thailand Post Company Limited