Page 119 - Demo 1
P. 119
Photosynthesis transforms solar energy into the chemical energy of a
carbohydrate. This process consists of a series of chemical reacons that require
carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) and store chemical energy in the form of
sugar. Light energy drives the reacons. Oxygen (O2) is a byproduct of
photosynthesis and is released into the atmosphere.
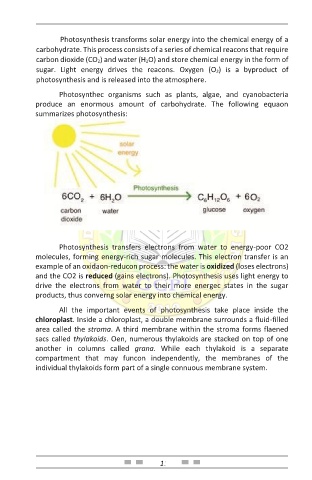
Photosynthec organisms such as plants, algae, and cyanobacteria
produce an enormous amount of carbohydrate. The following equaon
summarizes photosynthesis:
Photosynthesis transfers electrons from water to energy-poor CO2
molecules, forming energy-rich sugar molecules. This electron transfer is an
example of an oxidaon-reducon process: the water is oxidized (loses electrons)
and the CO2 is reduced (gains electrons). Photosynthesis uses light energy to
drive the electrons from water to their more energec states in the sugar
products, thus converng solar energy into chemical energy.
All the important events of photosynthesis take place inside the
chloroplast. Inside a chloroplast, a double membrane surrounds a fluid-filled
area called the stroma. A third membrane within the stroma forms flaened
sacs called thylakoids. Oen, numerous thylakoids are stacked on top of one
another in columns called grana. While each thylakoid is a separate
compartment that may funcon independently, the membranes of the
individual thylakoids form part of a single connuous membrane system.
111