Page 33 - ITGC_Audit Guides
P. 33
Microsoft, Google, or IBM, provides a platform on which organizations can quickly develop
their applications.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) – provides hardware and software tools (platform) for creating
software and applications. This structure is suitable for organizations that want to host and
run applications in the cloud without having to manage the infrastructure (i.e., storage,
updates, O/S). Providers of PaaS include, among others, Microsoft Google and AWS.
Software as a Service (SaaS) – an application delivered through the cloud available over
the internet, usually for a set fee. This model allows the greatest flexibility to the recipient
organization. Providers of SaaS include Google Apps, Netsuite, Salesforce.com,
ServiceNow, Workday, Dropbox, and DocuSign, among others.
Although external providers use these terms to market and explain their services and
approaches, an organization’s IT department may also use the terms if they offer such services.
The term “cloud” describes how data and information is stored and accessed over the internet,
but simplistically, it is the use of someone else’s computer network. The use of the term cloud is a
recognition that network architecture is largely irrelevant to most consumers of IT services, from
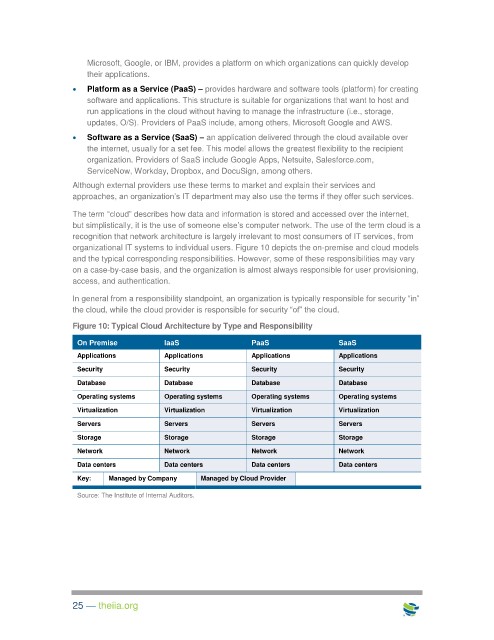
organizational IT systems to individual users. Figure 10 depicts the on-premise and cloud models
and the typical corresponding responsibilities. However, some of these responsibilities may vary
on a case-by-case basis, and the organization is almost always responsible for user provisioning,
access, and authentication.
In general from a responsibility standpoint, an organization is typically responsible for security “in”
the cloud, while the cloud provider is responsible for security “of” the cloud.
Figure 10: Typical Cloud Architecture by Type and Responsibility
On Premise IaaS PaaS SaaS
Applications Applications Applications Applications
Security Security Security Security
Database Database Database Database
Operating systems Operating systems Operating systems Operating systems
Virtualization Virtualization Virtualization Virtualization
Servers Servers Servers Servers
Storage Storage Storage Storage
Network Network Network Network
Data centers Data centers Data centers Data centers
Key: Managed by Company Managed by Cloud Provider
Source: The Institute of Internal Auditors.
25 — theiia.org