Page 35 - ITGC_Audit Guides
P. 35
Some versions of these protocols have an additional security or encryption, signified by the letter
“S,” such as SFTP, FTP via Secure Shell connection (SSH), or HTTPS. It is important for an
organization to understand the applicable secure protocol requirements in relation to regulations,
policies, and governing standards (e.g., NIST, Payment Card Industry [PCI] Data Security
Standard [DSS]).
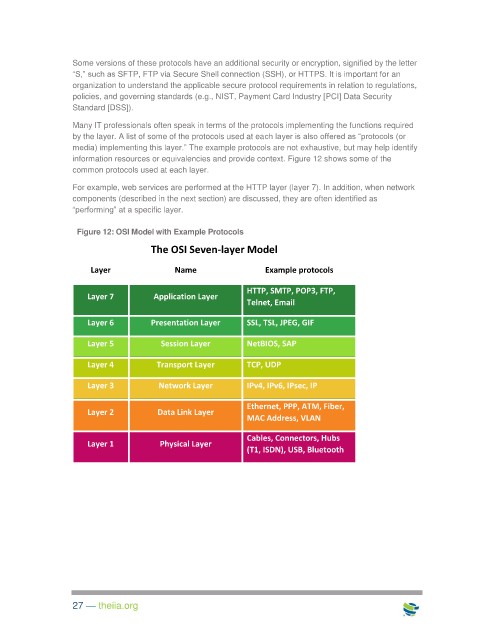
Many IT professionals often speak in terms of the protocols implementing the functions required
by the layer. A list of some of the protocols used at each layer is also offered as “protocols (or
media) implementing this layer.” The example protocols are not exhaustive, but may help identify
information resources or equivalencies and provide context. Figure 12 shows some of the
common protocols used at each layer.
For example, web services are performed at the HTTP layer (layer 7). In addition, when network
components (described in the next section) are discussed, they are often identified as
“performing” at a specific layer.
Figure 12: OSI Model with Example Protocols
The OSI Seven-layer Model
Layer Name Example protocols
HTTP, SMTP, POP3, FTP,
Layer 7 Application Layer
Telnet, Email
Layer 6 Presentation Layer SSL, TSL, JPEG, GIF
Layer 5 Session Layer NetBIOS, SAP
Layer 4 Transport Layer TCP, UDP
Layer 3 Network Layer IPv4, IPv6, IPsec, IP
Ethernet, PPP, ATM, Fiber,
Layer 2 Data Link Layer
MAC Address, VLAN
Cables, Connectors, Hubs
Layer 1 Physical Layer
(T1, ISDN), USB, Bluetooth
27 — theiia.org