Page 557 - ITGC_Audit Guides
P. 557
GTAG — BCM Requirements
• loss of it data center: Develop plan to manu- B. Determining RTO and RPO Based on
ally perform work processes until IT systems can be Business Impact
restored. Also, develop IT disaster recovery plans to The second step in a BIA is to identify the type of business
restore IT systems at alternative site. impact if the business process cannot be performed. Below
are some types of business impacts:
The BCM sponsor and an appropriate team of managers • Health and safety (e.g., injury).
must review and approve the BC risk assessment and BC risk • Environmental (e.g., spill).
mitigation strategies. Since management must act to address • Customer service (e.g., loss of customers).
the risks, it is critical that management approve the BC risk • Financial (e.g., penalties).
assessment and ensure the BC risk mitigation plan is funded, • Regulatory/legal (e.g., governmental action).
implemented, and tested periodically. • Reputation (e.g., loss of image).
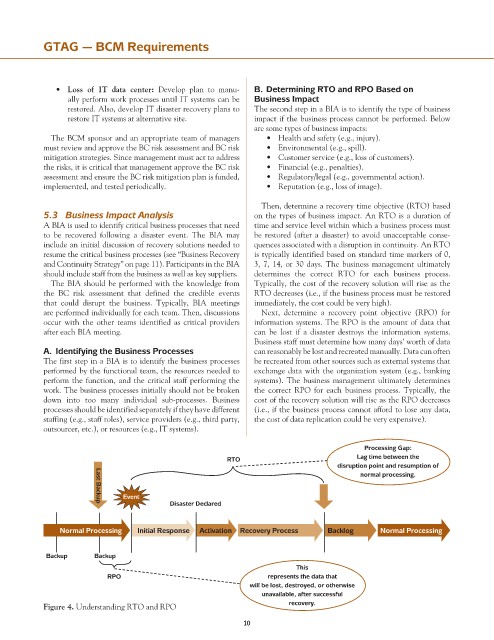
Then, determine a recovery time objective (RTO) based
5.3 Business Impact Analysis on the types of business impact. An RTO is a duration of
A BIA is used to identify critical business processes that need time and service level within which a business process must
to be recovered following a disaster event. The BIA may be restored (after a disaster) to avoid unacceptable conse-
include an initial discussion of recovery solutions needed to quences associated with a disruption in continuity. An RTO
resume the critical business processes (see “Business Recovery is typically identified based on standard time markers of 0,
and Continuity Strategy” on page 11). Participants in the BIA 3, 7, 14, or 30 days. The business management ultimately
should include staff from the business as well as key suppliers. determines the correct RTO for each business process.
The BIA should be performed with the knowledge from Typically, the cost of the recovery solution will rise as the
the BC risk assessment that defined the credible events RTO decreases (i.e., if the business process must be restored
that could disrupt the business. Typically, BIA meetings immediately, the cost could be very high).
are performed individually for each team. Then, discussions Next, determine a recovery point objective (RPO) for
occur with the other teams identified as critical providers information systems. The RPO is the amount of data that
after each BIA meeting. can be lost if a disaster destroys the information systems.
Business staff must determine how many days’ worth of data
A. Identifying the Business Processes can reasonably be lost and recreated manually. Data can often
The first step in a BIA is to identify the business processes be recreated from other sources such as external systems that
performed by the functional team, the resources needed to exchange data with the organization system (e.g., banking
perform the function, and the critical staff performing the systems). The business management ultimately determines
work. The business processes initially should not be broken the correct RPO for each business process. Typically, the
down into too many individual sub-processes. Business cost of the recovery solution will rise as the RPO decreases
processes should be identified separately if they have different (i.e., if the business process cannot afford to lose any data,
staffing (e.g., staff roles), service providers (e.g., third party, the cost of data replication could be very expensive).
outsourcer, etc.), or resources (e.g., IT systems).
Processing Gap:
RTO Lag time between the
disruption point and resumption of
normal processing.
Event
Disaster Declared
Last Backup
Normal Processing Initial Response Activation Recovery Process Backlog Normal Processing
Backup Backup
This
RPO represents the data that
will be lost, destroyed, or otherwise
unavailable, after successful
Figure 4. Understanding RTO and RPO recovery.
10