Page 378 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 378
Carcinogenesis: Mechanisms and Models Chapter | 20 345
VetBooks.ir
1
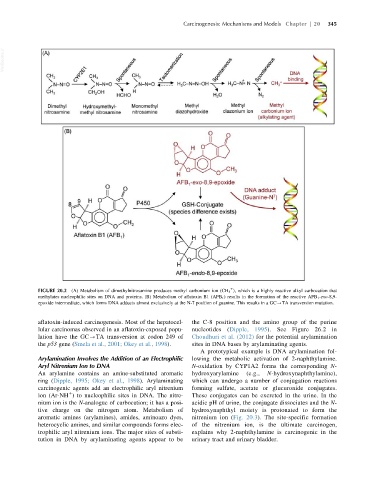
FIGURE 20.2 (A) Metabolism of dimethylnitrosamine produces methyl carbonium ion (CH 3 ), which is a highly reactive alkyl carbocation that
methylates nucleophilic sites on DNA and proteins. (B) Metabolism of aflatoxin B1 (AFB 1 ) results in the formation of the reactive AFB 1 -exo-8,9-
epoxide intermediate, which forms DNA adducts almost exclusively at the N-7 position of guanine. This results in a GC-TA transversion mutation.
aflatoxin-induced carcinogenesis. Most of the hepatocel- the C-8 position and the amino group of the purine
lular carcinomas observed in an aflatoxin-exposed popu- nucleotides (Dipple, 1995). See Figure 26.2 in
lation have the GC-TA transversion at codon 249 of Choudhuri et al. (2012) for the potential arylamination
the p53 gene (Smela et al., 2001; Okey et al., 1998). sites in DNA bases by arylaminating agents.
A prototypical example is DNA arylamination fol-
Arylamination Involves the Addition of an Electrophilic lowing the metabolic activation of 2-naphthylamine.
Aryl Nitrenium Ion to DNA N-oxidation by CYP1A2 forms the corresponding N-
An arylamine contains an amine-substituted aromatic hydroxyarylamine (e.g., N-hydroxynaphthylamine),
ring (Dipple, 1995; Okey et al., 1998). Arylaminating which can undergo a number of conjugation reactions
carcinogenic agents add an electrophilic aryl nitrenium forming sulfate, acetate or glucuronide conjugates.
1
ion (Ar-NH ) to nucleophilic sites in DNA. The nitre- These conjugates can be excreted in the urine. In the
nium ion is the N-analogue of carbocation; it has a posi- acidic pH of urine, the conjugate dissociates and the N-
tive charge on the nitrogen atom. Metabolism of hydroxynaphthyl moiety is protonated to form the
aromatic amines (arylamines), amides, aminoazo dyes, nitrenium ion (Fig. 20.3). The site-specific formation
heterocyclic amines, and similar compounds forms elec- of the nitrenium ion, is the ultimate carcinogen,
trophilic aryl nitrenium ions. The major sites of substi- explains why 2-naphthylamine is carcinogenic in the
tution in DNA by arylaminating agents appear to be urinary tract and urinary bladder.