Page 161 - Clinical Manual of Small Animal Endosurgery
P. 161
Operative Laparoscopy 149
(a)
(b)
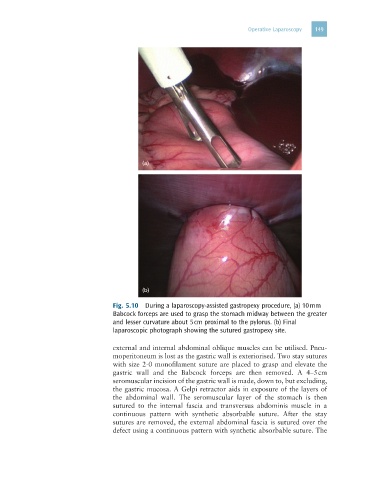
Fig. 5.10 During a laparoscopy-assisted gastropexy procedure, (a) 10 mm
Babcock forceps are used to grasp the stomach midway between the greater
and lesser curvature about 5 cm proximal to the pylorus. (b) Final
laparoscopic photograph showing the sutured gastropexy site.
external and internal abdominal oblique muscles can be utilised. Pneu-
moperitoneum is lost as the gastric wall is exteriorised. Two stay sutures
with size 2-0 monofilament suture are placed to grasp and elevate the
gastric wall and the Babcock forceps are then removed. A 4–5 cm
seromuscular incision of the gastric wall is made, down to, but excluding,
the gastric mucosa. A Gelpi retractor aids in exposure of the layers of
the abdominal wall. The seromuscular layer of the stomach is then
sutured to the internal fascia and transversus abdominis muscle in a
continuous pattern with synthetic absorbable suture. After the stay
sutures are removed, the external abdominal fascia is sutured over the
defect using a continuous pattern with synthetic absorbable suture. The