Page 57 - Live-cellanalysis handbook
P. 57
Kinetic Chemotaxis Assays
Immune cell chemotaxis – non-adherent cells
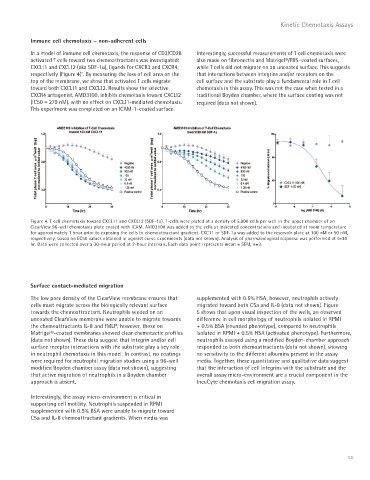
In a model of immune cell chemotaxis, the response of CD3/CD28 Interestingly, successful measurements of T cell chemotaxis were
activated T cells toward two chemoattractants was investigated: also made on fibronectin and Matrigel®/FBS–coated surfaces,
CXCL11 and CXCL12 (aka SDF-1a), ligands for CXCR3 and CXCR4, while T cells did not migrate on an uncoated surface. This suggests
2
respectively (Figure 4) . By measuring the loss of cell area on the that interactions between integrins and/or receptors on the
top of the membrane, we show that activated T cells migrate cell surface and the substrate play a fundamental role in T cell
toward both CXCL11 and CXCL12. Results show the selective chemotaxis in this assay. This was not the case when tested in a
CXCR4 antagonist, AMD3100, inhibits chemotaxis toward CXCL12 traditional Boyden chamber, where the surface coating was not
(IC50 = 279 nM), with no effect on CXCL11-mediated chemotaxis. required (data not shown).
This experiment was completed on an ICAM-1–coated surface.
Figure 4. T cell chemotaxis toward CXCL11 and CXCL12 (SDF-1a). T-cells were plated at a density of 5,000 cells per well in the upper chamber of an
ClearView 96-well chemotaxis plate coated with ICAM. AMD3100 was added to the cells at indicated concentrations and incubated at room temperature
for approximately 1 hour prior to exposing the cells to chemoattractant gradient. CXC11 or SDF-1a was added to the reservoir plate at 100 nM or 50 nM,
respectively, based on EC50 values obtained in agonist curve experiments (data not shown). Analysis of pharmacological response was performed at t=30
hr. Data were collected over a 30-hour period at 2-hour intervals. Each data point represents mean ± SEM, n=3.
Surface contact-mediated migration
The low pore density of the ClearView membrane ensures that supplemented with 0.5% HSA, however, neutrophils actively
cells must migrate across the biologically relevant surface migrated toward both C5a and IL-8 (data not shown). Figure
towards the chemoattractant. Neutrophils seeded on an 5 shows that upon visual inspection of the wells, an observed
uncoated ClearView membrane were unable to migrate towards difference in cell morphology of neutrophils isolated in RPMI
the chemoattractants IL-8 and fMLP; however, those on + 0.5% BSA (rounded phenotype), compared to neutrophils
Matrigel®-coated membranes showed clear chemotactic profiles isolated in RPMI + 0.5% HSA (activated phenotype). Furthermore,
(data not shown). These data suggest that integrin and/or cell neutrophils assayed using a modified Boyden-chamber approach
surface receptor interactions with the substrate play a key role responded to both chemoattractants (data not shown), showing
in neutrophil chemotaxis in this model. In contrast, no coatings no sensitivity to the different albumins present in the assay
were required for neutrophil migration studies using a 96-well media. Together, these quantitative and qualitative data suggest
modified Boyden chamber assay (data not shown), suggesting that the interaction of cell integrins with the substrate and the
that active migration of neutrophils in a Boyden chamber overall assay micro-environment are a crucial component in the
approach is absent. IncuCyte chemotaxis cell migration assay.
Interestingly, the assay micro-environment is critical in
supporting cell motility. Neutrophils suspended in RPMI
supplemented with 0.5% BSA were unable to migrate toward
C5a and IL-8 chemoattractant gradients. When media was
55