Page 17 - Rapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice, 2nd Edition
P. 17
Principles of Electrocardiography
THE PRECORDIAL OR CHEST LEADS GENESIS OF THE NORMAL ECG
(V LEADS)
The ECG waveforms are generated by the spread
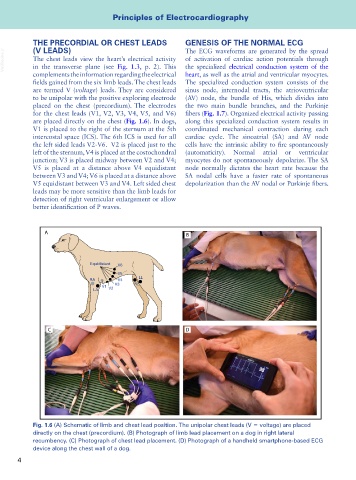
VetBooks.ir The chest leads view the heart’s electrical activity of activation of cardiac action potentials through
the specialized electrical conduction system of the
in the transverse plane (see Fig. 1.3, p. 2). This
complements the information regarding the electrical heart, as well as the atrial and ventricular myocytes.
fields gained from the six limb leads. The chest leads The specialized conduction system consists of the
are termed V (voltage) leads. They are considered sinus node, internodal tracts, the atrioventricular
to be unipolar with the positive exploring electrode (AV) node, the bundle of His, which divides into
placed on the chest (precordium). The electrodes the two main bundle branches, and the Purkinje
for the chest leads (V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, and V6) fibers (Fig. 1.7). Organized electrical activity passing
are placed directly on the chest (Fig. 1.6). In dogs, along this specialized conduction system results in
V1 is placed to the right of the sternum at the 5th coordinated mechanical contraction during each
intercostal space (ICS). The 6th ICS is used for all cardiac cycle. The sinoatrial (SA) and AV node
the left sided leads V2-V6. V2 is placed just to the cells have the intrinsic ability to fire spontaneously
left of the sternum, V4 is placed at the costochondral (automaticity). Normal atrial or ventricular
junction; V3 is placed midway between V2 and V4; myocytes do not spontaneously depolarize. The SA
V5 is placed at a distance above V4 equidistant node normally dictates the heart rate because the
between V3 and V4; V6 is placed at a distance above SA nodal cells have a faster rate of spontaneous
V5 equidistant between V3 and V4. Left sided chest depolarization than the AV nodal or Purkinje fibers.
leads may be more sensitive than the limb leads for
detection of right ventricular enlargement or allow
better identification of P waves.
A
B
Equidistant V6
V5
RA V4 LL
V3 RL
V1
LA V2
C D
Fig. 1.6 (A) Schematic of limb and chest lead position. The unipolar chest leads (V = voltage) are placed
directly on the chest (precordium). (B) Photograph of limb lead placement on a dog in right lateral
recumbency. (C) Photograph of chest lead placement. (D) Photograph of a handheld smartphone-based ECG
device along the chest wall of a dog.
4