Page 85 - Rapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice, 2nd Edition
P. 85
Answer 22 ECG Cases
Answer 22
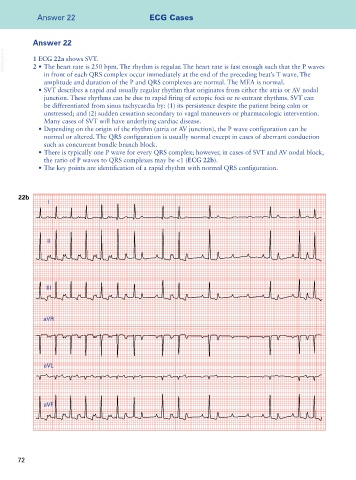
VetBooks.ir 1 ECG 22a shows SVT.
2 • The heart rate is 250 bpm. The rhythm is regular. The heart rate is fast enough such that the P waves
in front of each QRS complex occur immediately at the end of the preceding beat’s T wave. The
amplitude and duration of the P and QRS complexes are normal. The MEA is normal.
• SVT describes a rapid and usually regular rhythm that originates from either the atria or AV nodal
junction. These rhythms can be due to rapid firing of ectopic foci or re-entrant rhythms. SVT can
be differentiated from sinus tachycardia by: (1) its persistence despite the patient being calm or
unstressed; and (2) sudden cessation secondary to vagal maneuvers or pharmacologic intervention.
Many cases of SVT will have underlying cardiac disease.
• Depending on the origin of the rhythm (atria or AV junction), the P wave configuration can be
normal or altered. The QRS configuration is usually normal except in cases of aberrant conduction
such as concurrent bundle branch block.
• There is typically one P wave for every QRS complex; however, in cases of SVT and AV nodal block,
the ratio of P waves to QRS complexes may be <1 (ECG 22b).
• The key points are identification of a rapid rhythm with normal QRS configuration.
22b
I
II
III
aVR
aVL
aVF
72