Page 93 - Rapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice, 2nd Edition
P. 93
Answer 27 ECG Cases
Answer 27
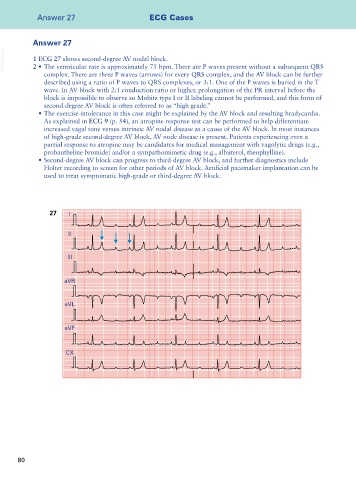
VetBooks.ir 1 ECG 27 shows second-degree AV nodal block.
2 • The ventricular rate is approximately 75 bpm. There are P waves present without a subsequent QRS
complex. There are three P waves (arrows) for every QRS complex, and the AV block can be further
described using a ratio of P waves to QRS complexes, or 3:1. One of the P waves is buried in the T
wave. In AV block with 2:1 conduction ratio or higher, prolongation of the PR interval before the
block is impossible to observe so Mobitz type I or II labeling cannot be performed, and this form of
second-degree AV block is often referred to as “high grade.”
• The exercise intolerance in this case might be explained by the AV block and resulting bradycardia.
As explained in ECG 9 (p. 54), an atropine response test can be performed to help differentiate
increased vagal tone versus intrinsic AV nodal disease as a cause of the AV block. In most instances
of high-grade second-degree AV block, AV node disease is present. Patients experiencing even a
partial response to atropine may be candidates for medical management with vagolytic drugs (e.g.,
probantheline bromide) and/or a sympathomimetic drug (e.g., albuterol, theophylline).
• Second-degree AV block can progress to third-degree AV block, and further diagnostics include
Holter recording to screen for other periods of AV block. Artificial pacemaker implantation can be
used to treat symptomatic high-grade or third-degree AV block.
27 I
II
III
aVR
aVL
aVF
CX
80