Page 29 - Feline Cardiology
P. 29
20 Section A: Clinical Entities
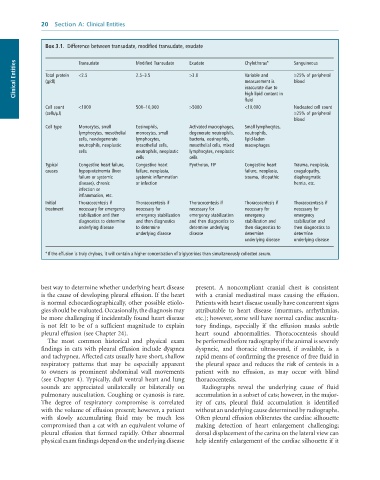
Box 3.1. Difference between transudate, modified transudate, exudate
Clinical Entities Total protein Transudate Modified Transudate Exudate Chylothorax* Sanguineous
>3.0
Variable and
<2.5
2.5–3.5
≥25% of peripheral
(g/dl)
blood
measurement is
inaccurate due to
high lipid content in
fluid
Cell count <1000 500–10,000 >5000 <10,000 Nucleated cell count
(cells/µl) ≥25% of peripheral
blood
Cell type Monocytes, small Eosinophils, Activated macrophages, Small lymphocytes,
lymphocytes, mesothelial monocytes, small degenerate neutrophils, neutrophils,
cells, nondegenerate lymphocytes, bacteria, eosinophils, lipid-laden
neutrophils, neoplastic mesothelial cells, mesothelial cells, mixed macrophages
cells neutrophils, neoplastic lymphocytes, neoplastic
cells cells
Typical Congestive heart failure, Congestive heart Pyothorax, FIP Congestive heart Trauma, neoplasia,
causes hypoproteinemia (liver failure, neoplasia, failure, neoplasia, coagulopathy,
failure or systemic systemic inflammation trauma, idiopathic diaphragmatic
disease), chronic or infection hernia, etc.
infection or
inflammation, etc.
Initial Thoracocentesis if Thoracocentesis if Thoracocentesis if Thoracocentesis if Thoracocentesis if
treatment necessary for emergency necessary for necessary for necessary for necessary for
stabilization and then emergency stabilization emergency stabilization emergency emergency
diagnostics to determine and then diagnostics and then diagnostics to stabilization and stabilization and
underlying disease to determine determine underlying then diagnostics to then diagnostics to
underlying disease disease determine determine
underlying disease underlying disease
* If the effusion is truly chylous, it will contain a higher concentration of triglycerides than simultaneously collected serum.
best way to determine whether underlying heart disease present. A noncompliant cranial chest is consistent
is the cause of developing pleural effusion. If the heart with a cranial mediastinal mass causing the effusion.
is normal echocardiographically, other possible etiolo- Patients with heart disease usually have concurrent signs
gies should be evaluated. Occasionally, the diagnosis may attributable to heart disease (murmurs, arrhythmias,
be more challenging if incidentally found heart disease etc.); however, some will have normal cardiac ausculta-
is not felt to be of a sufficient magnitude to explain tory findings, especially if the effusion masks subtle
pleural effusion (see Chapter 24). heart sound abnormalities. Thoracocentesis should
The most common historical and physical exam be performed before radiography if the animal is severely
findings in cats with pleural effusion include dyspnea dyspneic, and thoracic ultrasound, if available, is a
and tachypnea. Affected cats usually have short, shallow rapid means of confirming the presence of free fluid in
respiratory patterns that may be especially apparent the pleural space and reduces the risk of centesis in a
to owners as prominent abdominal wall movements patient with no effusion, as may occur with blind
(see Chapter 4). Typically, dull ventral heart and lung thoracocentesis.
sounds are appreciated unilaterally or bilaterally on Radiographs reveal the underlying cause of fluid
pulmonary auscultation. Coughing or cyanosis is rare. accumulation in a subset of cats; however, in the major-
The degree of respiratory compromise is correlated ity of cats, pleural fluid accumulation is identified
with the volume of effusion present; however, a patient without an underlying cause determined by radiographs.
with slowly accumulating fluid may be much less Often pleural effusion obliterates the cardiac silhouette
compromised than a cat with an equivalent volume of making detection of heart enlargement challenging;
pleural effusion that formed rapidly. Other abnormal dorsal displacement of the carina on the lateral view can
physical exam findings depend on the underlying disease help identify enlargement of the cardiac silhouette if it