Page 34 - Feline Cardiology
P. 34
26 Section A: Clinical Entities
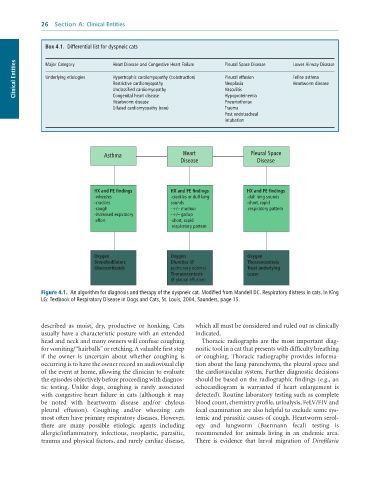
Box 4.1. Differential list for dyspneic cats
Clinical Entities Major Category Heart Disease and Congestive Heart Failure Pleural Space Disease Lower Airway Disease
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (±obstruction)
Pleural effusion
Underlying etiologies
Feline asthma
Neoplasia
Heartworm disease
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
Unclassified cardiomyopathy
Vasculitis
Congenital heart disease
Pneumothorax
Heartworm disease Hypoproteinemia
Dilated cardiomyopathy (rare) Trauma
Post endotracheal
intubation
Asthma Heart Pleural Space
Disease Disease
HX and PE findings HX and PE findings HX and PE findings
-wheezes -crackles or dull lung -dull lung sounds
-crackles sounds -short, rapid
-cough -+/– murmur respiratory pattern
-increased expiratory -+/– gallop
effort -short, rapid
respiratory pattern
Oxygen Oxygen Oxygen
Bronchodilators Diuretics (if Thoracocentesis
Glucocorticoids pulmonary edema) Treat underlying
Thoracocentesis cause
(if pleural effusion)
Figure 4.1. An algorithm for diagnosis and therapy of the dyspneic cat. Modified from Mandell DC. Respiratory distress in cats. In King
LG: Textbook of Respiratory Disease in Dogs and Cats, St. Louis, 2004, Saunders, page 15.
described as moist, dry, productive or honking. Cats which all must be considered and ruled out as clinically
usually have a characteristic posture with an extended indicated.
head and neck and many owners will confuse coughing Thoracic radiographs are the most important diag-
for vomiting/“hairballs” or retching. A valuable first step nostic tool in a cat that presents with difficulty breathing
if the owner is uncertain about whether coughing is or coughing. Thoracic radiography provides informa-
occurring is to have the owner record an audiovisual clip tion about the lung parenchyma, the pleural space and
of the event at home, allowing the clinician to evaluate the cardiovascular system. Further diagnostic decisions
the episodes objectively before proceeding with diagnos- should be based on the radiographic findings (e.g., an
tic testing. Unlike dogs, coughing is rarely associated echocardiogram is warranted if heart enlargement is
with congestive heart failure in cats (although it may detected). Routine laboratory testing such as complete
be noted with heartworm disease and/or chylous blood count, chemistry profile, urinalysis, FeLV/FIV and
pleural effusion). Coughing and/or wheezing cats fecal examination are also helpful to exclude some sys-
most often have primary respiratory diseases. However, temic and parasitic causes of cough. Heartworm serol-
there are many possible etiologic agents including ogy and lungworm (Baermann fecal) testing is
allergic/inflammatory, infectious, neoplastic, parasitic, recommended for animals living in an endemic area.
trauma and physical factors, and rarely cardiac disease, There is evidence that larval migration of Dirofilaria