Page 417 - Feline Cardiology
P. 417
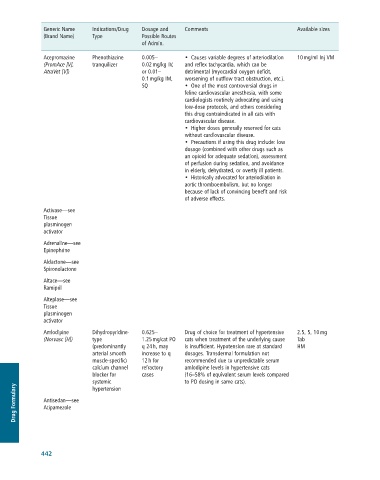
Generic Name Indications/Drug Dosage and Comments Available sizes
(Brand Name) Type Possible Routes
of Admin.
Acepromazine Phenothiazine 0.005– • Causes variable degrees of arteriodilation 10 mg/ml Inj VM
(PromAce [V], tranquilizer 0.02 mg/kg IV, and reflex tachycardia, which can be
AtraVet [V]) or 0.01– detrimental (myocardial oxygen deficit,
0.1 mg/kg IM, worsening of outflow tract obstruction, etc.).
SQ • One of the most controversial drugs in
feline cardiovascular anesthesia, with some
cardiologists routinely advocating and using
low-dose protocols, and others considering
this drug contraindicated in all cats with
cardiovascular disease.
• Higher doses generally reserved for cats
without cardiovascular disease.
• Precautions if using this drug include: low
dosage (combined with other drugs such as
an opioid for adequate sedation), assessment
of perfusion during sedation, and avoidance
in elderly, dehydrated, or overtly ill patients.
• Historically advocated for arteriodilation in
aortic thromboembolism, but no longer
because of lack of convincing benefit and risk
of adverse effects.
Activase—see
Tissue
plasminogen
activator
Adrenaline—see
Epinephrine
Aldactone—see
Spironolactone
Altace—see
Ramipril
Alteplase—see
Tissue
plasminogen
activator
Amlodipine Dihydropyridine- 0.625– Drug of choice for treatment of hypertensive 2.5, 5, 10 mg
(Norvasc [H]) type 1.25 mg/cat PO cats when treatment of the underlying cause Tab
(predominantly q 24 h, may is insufficient. Hypotension rare at standard HM
arterial smooth increase to q dosages. Transdermal formulation not
muscle-specific) 12 h for recommended due to unpredictable serum
calcium channel refractory amlodipine levels in hypertensive cats
blocker for cases (16–58% of equivalent serum levels compared
systemic to PO dosing in same cats).
Drug Formulary Antisedan—see
hypertension
Atipamezole
442