Page 58 - Feline Cardiology
P. 58
Chapter 7: Echocardiography 53
A Diagnostic Testing
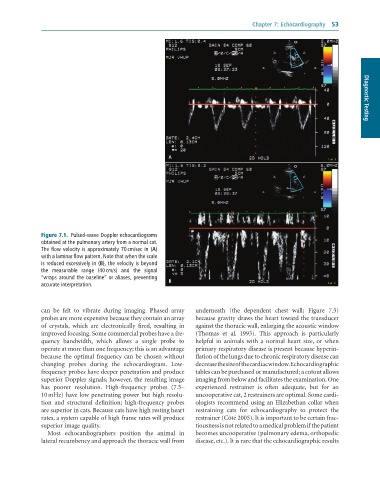
Figure 7.1. Pulsed-wave Doppler echocardiograms
obtained at the pulmonary artery from a normal cat.
The flow velocity is approximately 70 cm/sec in (A)
with a laminar flow pattern. Note that when the scale
is reduced excessively in (B), the velocity is beyond
the measurable range (40 cm/s) and the signal
“wraps around the baseline” or aliases, preventing
B
accurate interpretation.
can be felt to vibrate during imaging. Phased array underneath (the dependent chest wall; Figure 7.3)
probes are more expensive because they contain an array because gravity draws the heart toward the transducer
of crystals, which are electronically fired, resulting in against the thoracic wall, enlarging the acoustic window
improved focusing. Some commercial probes have a fre- (Thomas et al. 1993). This approach is particularly
quency bandwidth, which allows a single probe to helpful in animals with a normal heart size, or when
operate at more than one frequency; this is an advantage primary respiratory disease is present because hyperin-
because the optimal frequency can be chosen without flation of the lungs due to chronic respiratory disease can
changing probes during the echocardiogram. Low- decrease the size of the cardiac window. Echocardiographic
frequency probes have deeper penetration and produce tables can be purchased or manufactured; a cutout allows
superior Doppler signals; however, the resulting image imaging from below and facilitates the examination. One
has poorer resolution. High-frequency probes (7.5– experienced restrainer is often adequate, but for an
10 mHz) have low penetrating power but high resolu- uncooperative cat, 2 restrainers are optimal. Some cardi-
tion and structural definition; high-frequency probes ologists recommend using an Elizabethan collar when
are superior in cats. Because cats have high resting heart restraining cats for echocardiography to protect the
rates, a system capable of high frame rates will produce restrainer (Côté 2005). It is important to be certain frac-
superior image quality. tiousness is not related to a medical problem if the patient
Most echocardiographers position the animal in becomes uncooperative (pulmonary edema, orthopedic
lateral recumbency and approach the thoracic wall from disease, etc.). It is rare that the echocardiographic results