Page 61 - Feline Cardiology
P. 61
56 Section B: Diagnostic Testing
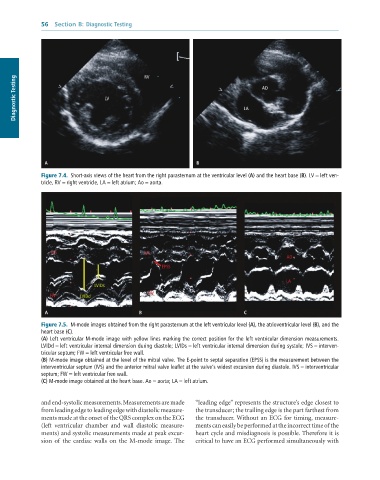
Diagnostic Testing LV RV LA AO
A B
Figure 7.4. Short-axis views of the heart from the right parasternum at the ventricular level (A) and the heart base (B). LV = left ven-
tricle, RV = right ventricle, LA = left atrium; Ao = aorta.
IVS IVS
AO
EPSS
LA
LVIDs
FW
FW LVIDd
A B C
Figure 7.5. M-mode images obtained from the right parasternum at the left ventricular level (A), the atrioventricular level (B), and the
heart base (C).
(A) Left ventricular M-mode image with yellow lines marking the correct position for the left ventricular dimension measurements.
LVIDd = left ventricular internal dimension during diastole; LVIDs = left ventricular internal dimension during systole; IVS = interven-
tricular septum; FW = left ventricular free wall.
(B) M-mode image obtained at the level of the mitral valve. The E-point to septal separation (EPSS) is the measurement between the
interventricular septum (IVS) and the anterior mitral valve leaflet at the valve’s widest excursion during diastole. IVS = interventricular
septum; FW = left ventricular free wall.
(C) M-mode image obtained at the heart base. Ao = aorta; LA = left atrium.
and end-systolic measurements. Measurements are made “leading edge” represents the structure’s edge closest to
from leading edge to leading edge with diastolic measure- the transducer; the trailing edge is the part farthest from
ments made at the onset of the QRS complex on the ECG the transducer. Without an ECG for timing, measure-
(left ventricular chamber and wall diastolic measure- ments can easily be performed at the incorrect time of the
ments) and systolic measurements made at peak excur- heart cycle and misdiagnosis is possible. Therefore it is
sion of the cardiac walls on the M-mode image. The critical to have an ECG performed simultaneously with