Page 66 - Feline Cardiology
P. 66
Chapter 7: Echocardiography 61
AO Diagnostic Testing
LV
LA
A
RA
LV
LA
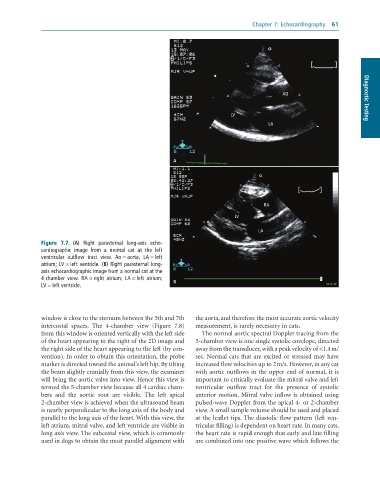
Figure 7.7. (A) Right parasternal long-axis echo-
cardiographic image from a normal cat at the left
ventricular outflow tract view. Ao = aorta, LA = left
atrium; LV = left ventricle. (B) Right parasternal long-
axis echocardiographic image from a normal cat at the
4-chamber view. RA = right atrium; LA = left atrium;
B
LV = left ventricle.
window is close to the sternum between the 5th and 7th the aorta, and therefore the most accurate aortic velocity
intercostal spaces. The 4-chamber view (Figure 7.8) measurement, is rarely necessary in cats.
from this window is oriented vertically with the left side The normal aortic spectral Doppler tracing from the
of the heart appearing to the right of the 2D image and 5-chamber view is one single systolic envelope, directed
the right side of the heart appearing to the left (by con- away from the transducer, with a peak velocity of <1.4 m/
vention). In order to obtain this orientation, the probe sec. Normal cats that are excited or stressed may have
marker is directed toward the animal’s left hip. By tilting increased flow velocities up to 2 m/s. However, in any cat
the beam slightly cranially from this view, the examiner with aortic outflows in the upper end of normal, it is
will bring the aortic valve into view. Hence this view is important to critically evaluate the mitral valve and left
termed the 5-chamber view because all 4 cardiac cham- ventricular outflow tract for the presence of systolic
bers and the aortic root are visible. The left apical anterior motion. Mitral valve inflow is obtained using
2-chamber view is achieved when the ultrasound beam pulsed-wave Doppler from the apical 4- or 2-chamber
is nearly perpendicular to the long axis of the body and view. A small sample volume should be used and placed
parallel to the long axis of the heart. With this view, the at the leaflet tips. The diastolic flow pattern (left ven-
left atrium, mitral valve, and left ventricle are visible in tricular filling) is dependent on heart rate. In many cats,
long axis view. The subcostal view, which is commonly the heart rate is rapid enough that early and late filling
used in dogs to obtain the most parallel alignment with are combined into one positive wave which follows the