Page 69 - Feline Cardiology
P. 69
64 Section B: Diagnostic Testing
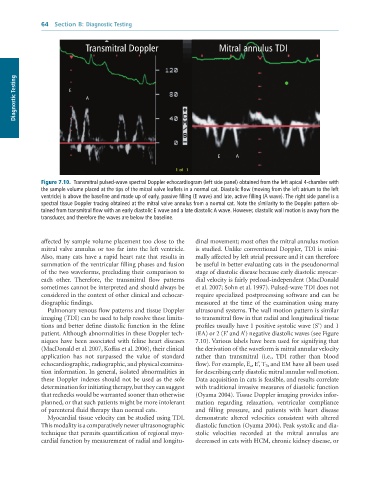
Transmitral Doppler Mitral annulus TDI
Diagnostic Testing E A
E A
Figure 7.10. Transmitral pulsed-wave spectral Doppler echocardiogram (left side panel) obtained from the left apical 4-chamber with
the sample volume placed at the tips of the mitral valve leaflets in a normal cat. Diastolic flow (moving from the left atrium to the left
ventricle) is above the baseline and made up of early, passive filling (E wave) and late, active filling (A wave). The right side panel is a
spectral tissue Doppler tracing obtained at the mitral valve annulus from a normal cat. Note the similarity to the Doppler pattern ob-
tained from transmitral flow with an early diastolic E wave and a late diastolic A wave. However, diastolic wall motion is away from the
transducer, and therefore the waves are below the baseline.
affected by sample volume placement too close to the dinal movement; most often the mitral annulus motion
mitral valve annulus or too far into the left ventricle. is studied. Unlike conventional Doppler, TDI is mini-
Also, many cats have a rapid heart rate that results in mally affected by left atrial pressure and it can therefore
summation of the ventricular filling phases and fusion be useful in better evaluating cats in the pseudonormal
of the two waveforms, precluding their comparison to stage of diastolic disease because early diastolic myocar-
each other. Therefore, the transmitral flow patterns dial velocity is fairly preload-independent (MacDonald
sometimes cannot be interpreted and should always be et al. 2007; Sohn et al. 1997). Pulsed-wave TDI does not
considered in the context of other clinical and echocar- require specialized postprocessing software and can be
diographic findings. measured at the time of the examination using many
Pulmonary venous flow patterns and tissue Doppler ultrasound systems. The wall motion pattern is similar
imaging (TDI) can be used to help resolve these limita- to transmitral flow in that radial and longitudinal tissue
tions and better define diastolic function in the feline profiles usually have 1 positive systolic wave (S’) and 1
patient. Although abnormalities in these Doppler tech- (EA) or 2 (E’ and A’) negative diastolic waves (see Figure
niques have been associated with feline heart diseases 7.10). Various labels have been used for signifying that
(MacDonald et al. 2007, Koffas et al. 2006), their clinical the derivation of the waveform is mitral annular velocity
application has not surpassed the value of standard rather than transmitral (i.e., TDI rather than blood
echocardiographic, radiographic, and physical examina- flow). For example, E a , E’, T E , and EM have all been used
tion information. In general, isolated abnormalities in for describing early diastolic mitral annular wall motion.
these Doppler indexes should not be used as the sole Data acquisition in cats is feasible, and results correlate
determination for initiating therapy, but they can suggest with traditional invasive measures of diastolic function
that rechecks would be warranted sooner than otherwise (Oyama 2004). Tissue Doppler imaging provides infor-
planned, or that such patients might be more intolerant mation regarding relaxation, ventricular compliance
of parenteral fluid therapy than normal cats. and filling pressure, and patients with heart disease
Myocardial tissue velocity can be studied using TDI. demonstrate altered velocities consistent with altered
This modality is a comparatively newer ultrasonographic diastolic function (Oyama 2004). Peak systolic and dia-
technique that permits quantification of regional myo- stolic velocities recorded at the mitral annulus are
cardial function by measurement of radial and longitu- decreased in cats with HCM, chronic kidney disease, or