Page 139 - Basic Monitoring in Canine and Feline Emergency Patients
P. 139
(A)
Gas, minerals
Vascular walls, organ
VetBooks.ir capsules, intestinal SV
serosa
Intestinal submucosa
Spleen
Prostate Liver
Spleen PV
Fat, lymph nodes
Liver, pancreas HV
Renal cortex RC
RM
Fat RP
Renal medulla, adrenal
glands Kidney
Vascular lumen
Bile, urine, pure fluid
(B) LOGIQ
S8
Spleen
SV
RM
RC RP
Liver
Fat Kidney
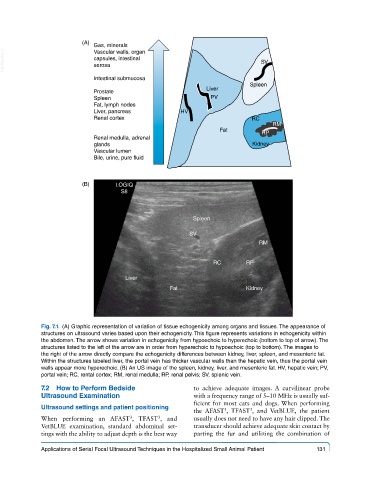
Fig. 7.1. (A) Graphic representation of variation of tissue echogenicity among organs and tissues. The appearance of
structures on ultrasound varies based upon their echogenicity. This figure represents variations in echogenicity within
the abdomen. The arrow shows variation in echogenicity from hypoechoic to hyperechoic (bottom to top of arrow). The
structures listed to the left of the arrow are in order from hyperechoic to hypoechoic (top to bottom). The images to
the right of the arrow directly compare the echogenicity differences between kidney, liver, spleen, and mesenteric fat.
Within the structures labeled liver, the portal vein has thicker vascular walls than the hepatic vein, thus the portal vein
walls appear more hyperechoic. (B) An US image of the spleen, kidney, liver, and mesenteric fat. HV, hepatic vein; PV,
portal vein; RC, rental cortex; RM, renal medulla; RP, renal pelvis; SV, splenic vein.
7.2 How to Perform Bedside to achieve adequate images. A curvilinear probe
Ultrasound Examination with a frequency range of 5–10 MHz is usually suf-
ficient for most cats and dogs. When performing
Ultrasound settings and patient positioning
3
the AFAST , TFAST , and VetBLUE, the patient
3
When performing an AFAST , TFAST , and usually does not need to have any hair clipped. The
3
3
VetBLUE examination, standard abdominal set- transducer should achieve adequate skin contact by
tings with the ability to adjust depth is the best way parting the fur and utilizing the combination of
Applications of Serial Focal Ultrasound Techniques in the Hospitalized Small Animal Patient 131