Page 264 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 264
Cardiovascular Toxicity Chapter | 14 231
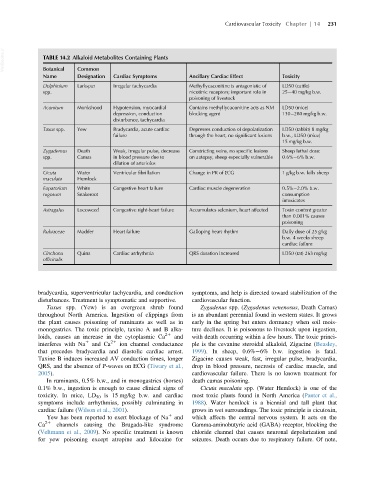
VetBooks.ir TABLE 14.2 Alkaloid Metabolites Containing Plants
Botanical
Designation
Name Common Cardiac Symptoms Ancillary Cardiac Effect Toxicity
Delphinium Larkspur Irregular tachycardia Methyllycaconitine is antagonistic of LD50 (cattle)
spp. nicotinic receptors; important role in 25 40 mg/kg b.w.
poisoning of livestock
Aconitum Monkshood Hypotension, myocardial Contains methyllycaconitine acts as NM LD50 (mice)
depression, conduction blocking agent 130 280 mg/kg b.w.
disturbance, tachycardia
Taxus spp. Yew Bradycardia, acute cardiac Depresses conduction of depolarization LD50 (rabbit) 8 mg/kg
failure through the heart, no significant lesions b.w., LD50 (mice)
15 mg/kg b.w.
Zygademus Death Weak, irregular pulse, decrease Constricting veins, no specific lesions Sheep lethal dose:
spp. Camas in blood pressure due to on autopsy, sheep especially vulnerable 0.6% 6% b.w.
dilation of arterioles
Cicuta Water Ventricular fibrillation Change in PR of ECG 1 g/kg b.w. kills sheep
maculata Hemlock
Eupatorium White Congestive heart failure Cardiac muscle degeneration 0.5% 2.0% b.w.
rugosum Snakeroot consumption
intoxicates
Astragalus Locoweed Congestive right-heart failure Accumulates selenium, heart affected Toxin content greater
than 0.001% causes
poisoning
Rubiaceae Madder Heart failure Galloping heart rhythm Daily dose of 25 g/kg
b.w. 4 weeks sheep
cardiac failure
Cinchona Quina Cardiac arrhythmia QRS duration increased LD50 (rat) 263 mg/kg
officinalis
bradycardia, superventricular tachycardia, and conduction symptoms, and help is directed toward stabilization of the
disturbances. Treatment is symptomatic and supportive. cardiovascular function.
Taxus spp. (Yew) is an evergreen shrub found Zygadenus spp. (Zygadenus venenosus, Death Camas)
throughout North America. Ingestion of clippings from is an abundant perennial found in western states. It grows
the plant causes poisoning of ruminants as well as in early in the spring but enters dormancy when soil mois-
monogastrics. The toxic principle, taxine A and B alka- ture declines. It is poisonous to livestock upon ingestion,
21
loids, causes an increase in the cytoplasmic Ca and with death occurring within a few hours. The toxic princi-
interferes with Na 1 and Ca 21 ion channel conductance ple is the cevanine steroidal alkaloid, Zigacine (Beasley,
that precedes bradycardia and diastolic cardiac arrest. 1999). In sheep, 0.6% 6% b.w. ingestion is fatal.
Taxine B induces increased AV conduction times, longer Zigacine causes weak, fast, irregular pulse, bradycardia,
QRS, and the absence of P-waves on ECG (Tiwary et al., drop in blood pressure, necrosis of cardiac muscle, and
2005). cardiovascular failure. There is no known treatment for
In ruminants, 0.5% b.w., and in monogastrics (horses) death camas poisoning.
0.1% b.w., ingestion is enough to cause clinical signs of Cicuta maculata spp. (Water Hemlock) is one of the
toxicity. In mice, LD 50 is 15 mg/kg b.w. and cardiac most toxic plants found in North America (Panter et al.,
symptoms include arrhythmias, possibly culminating in 1988). Water hemlock is a biennial and tall plant that
cardiac failure (Wilson et al., 2001). grows in wet surroundings. The toxic principle is cicutoxin,
1
Yew has been reported to exert blockage of Na and which affects the central nervous system. It acts on the
21
Ca channels causing the Brugada-like syndrome Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor, blocking the
(Veltmann et al., 2009). No specific treatment is known chloride channel that causes neuronal depolarization and
for yew poisoning except atropine and lidocaine for seizures. Death occurs due to respiratory failure. Of note,