Page 262 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 262
Cardiovascular Toxicity Chapter | 14 229
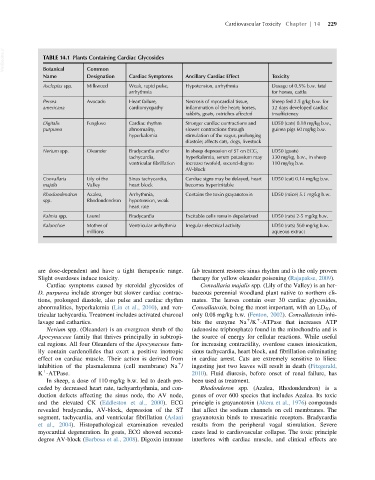
VetBooks.ir TABLE 14.1 Plants Containing Cardiac Glycosides
Botanical
Name Common Cardiac Symptoms Ancillary Cardiac Effect Toxicity
Designation
Asclepias spp. Milkweed Weak, rapid pulse, Hypotension, arrhythmia Dosage of 0.5% b.w. fatal
arrhythmia for horses, cattle
Persea Avocado Heart failure, Necrosis of myocardial tissue, Sheep fed 2.5 g/kg b.w. for
americana cardiomyopathy inflammation of the heart; horses, 32 days developed cardiac
rabbits, goats, ostriches affected insufficiency
Digitalis Foxglove Cardiac rhythm Stronger cardiac contractions and LD50 (cats) 0.18 mg/kg b.w.,
purpurea abnormality, slower contractions through guinea pigs 60 mg/kg b.w.
hyperkalemia stimulation of the vagus, prolonging
diastole; affects cats, dogs, livestock
Nerium spp. Oleander Bradycardia and/or In sheep depression of ST on ECG, LD50 (goats)
tachycardia, hyperkalemia, serum potassium may 330 mg/kg, b.w., in sheep
ventricular fibrillation increase twofold, second-degree 110 mg/kg b.w.
AV-block
Convallaria Lily of the Sinus tachycardia, Cardiac signs may be delayed, heart LD50 (cat) 0.14 mg/kg b.w.
majalis Valley heart block becomes hyperirritable
Rhodondendron Azalea, Arrhythmia, Contains the toxin grayanotoxin LD50 (mice) 5.1 mg/kg b.w.
spp. Rhodondendron hypotension, weak
heart rate
Kalmia spp. Laurel Bradycardia Excitable cells remain depolarized LD50 (rats) 2-5 mg/kg b.w.
Kalanchoe Mother of Ventricular arrhythmia Irregular electrical activity LD50 (rats) 560 mg/kg b.w.
millions aqueous extract
are dose-dependent and have a tight therapeutic range. fab treatment restores sinus rhythm and is the only proven
Slight overdoses induce toxicity. therapy for yellow oleander poisoning (Rajapakse, 2009).
Cardiac symptoms caused by steroidal glycosides of Convallaria majalis spp. (Lily of the Valley) is an her-
D. purpurea include stronger but slower cardiac contrac- baceous perennial woodland plant native to northern cli-
tions, prolonged diastole, also pulse and cardiac rhythm mates. The leaves contain over 30 cardiac glycosides,
abnormalities, hyperkalemia (Lin et al., 2010), and ven- Convallatoxin, being the most important, with an LD 50 of
tricular tachycardia. Treatment includes activated charcoal only 0.08 mg/kg b.w. (Fenton, 2002). Convallatoxin inhi-
1 1
lavage and cathartics. bits the enzyme Na /K -ATPase that increases ATP
Nerium spp. (Oleander) is an evergreen shrub of the (adenosine triphosphate) found in the mitochondria and is
Apocynaceae family that thrives principally in subtropi- the source of energy for cellular reactions. While useful
cal regions. All four Oleanders of the Apocynaceae fam- for increasing contractility, overdose causes intoxication,
ily contain cardenolides that exert a positive inotropic sinus tachycardia, heart block, and fibrillation culminating
effect on cardiac muscle. Their action is derived from in cardiac arrest. Cats are extremely sensitive to lilies:
1
inhibition of the plasmalemma (cell membrane) Na / ingesting just two leaves will result in death (Fitzgerald,
1
K -ATPase. 2010). Fluid diuresis, before onset of renal failure, has
In sheep, a dose of 110 mg/kg b.w. led to death pre- been used as treatment.
ceded by decreased heart rate, tachyarrhythmia, and con- Rhodonderon spp. (Azalea, Rhodondendron) is a
duction defects affecting the sinus node, the AV node, genus of over 600 species that includes Azalea. Its toxic
and the elevated CK (Eddleston et al., 2000). ECG principle is grayanotoxin (Akera et al., 1976) compounds
revealed bradycardia, AV-block, depression of the ST that affect the sodium channels on cell membranes. The
segment, tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation (Aslani grayanotoxin binds to muscarinic receptors. Bradycardia
et al., 2004). Histopathological examination revealed results from the peripheral vagal stimulation. Severe
myocardial degeneration. In goats, ECG showed second- cases lead to cardiovascular collapse. The toxic principle
degree AV-block (Barbosa et al., 2008). Digoxin immune interferes with cardiac muscle, and clinical effects are