Page 274 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 274
Liver Toxicity Chapter | 15 241
VetBooks.ir
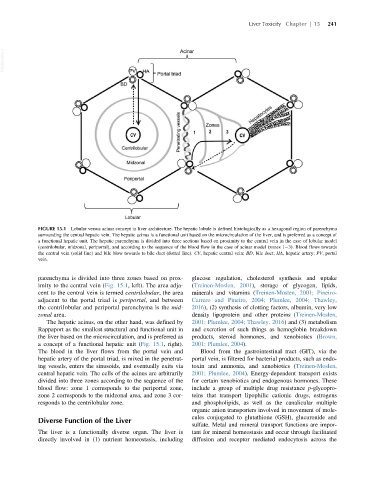
FIGURE 15.1 Lobular versus acinar concept in liver architecture. The hepatic lobule is defined histologically as a hexagonal region of parenchyma
surrounding the central hepatic vein. The hepatic acinus is a functional unit based on the microcirculation of the liver, and is preferred as a concept of
a functional hepatic unit. The hepatic parenchyma is divided into three sections based on proximity to the central vein in the case of lobular model
(centrilobular, midzonal, periportal), and according to the sequence of the blood flow in the case of acinar model (zones 1 3). Blood flows towards
the central vein (solid line) and bile blow towards to bile duct (dotted line). CV, hepatic central vein; BD, bile duct; HA, hepatic artery; PV, portal
vein.
parenchyma is divided into three zones based on prox- glucose regulation, cholesterol synthesis and uptake
imitytothe centralvein(Fig. 15.1,left).The area adja- (Treinen-Moslen, 2001), storage of glycogen, lipids,
cent to the central vein is termed centrilobular,the area minerals and vitamins (Treinen-Moslen, 2001; Pineiro-
adjacent to the portal triad is periportal, and between Carrero and Pineiro, 2004; Plumlee, 2004; Thawley,
the centrilobular and periportal parenchyma is the mid- 2016), (2) synthesis of clotting factors, albumin, very low
zonal area. density lipoprotein and other proteins (Treinen-Moslen,
The hepatic acinus, on the other hand, was defined by 2001; Plumlee, 2004; Thawley, 2016) and (3) metabolism
Rappaport as the smallest structural and functional unit in and excretion of such things as hemoglobin breakdown
the liver based on the microcirculation, and is preferred as products, steroid hormones, and xenobiotics (Brown,
a concept of a functional hepatic unit (Fig. 15.1, right). 2001; Plumlee, 2004).
The blood in the liver flows from the portal vein and Blood from the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), via the
hepatic artery of the portal triad, is mixed in the penetrat- portal vein, is filtered for bacterial products, such as endo-
ing vessels, enters the sinusoids, and eventually exits via toxin and ammonia, and xenobiotics (Treinen-Moslen,
central hepatic vein. The cells of the acinus are arbitrarily 2001; Plumlee, 2004). Energy-dependent transport exists
divided into three zones according to the sequence of the for certain xenobiotics and endogenous hormones. These
blood flow: zone 1 corresponds to the periportal zone, include a group of multiple drug resistance p-glycopro-
zone 2 corresponds to the midzonal area, and zone 3 cor- teins that transport lipophilic cationic drugs, estrogens
responds to the centrilobular zone. and phospholipids, as well as the canalicular multiple
organic anion transporters involved in movement of mole-
cules conjugated to glutathione (GSH), glucuronide and
Diverse Function of the Liver
sulfate. Metal and mineral transport functions are impor-
The liver is a functionally diverse organ. The liver is tant for mineral homeostasis and occur through facilitated
directly involved in (1) nutrient homeostasis, including diffusion and receptor mediated endocytosis across the