Page 296 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 296
Renal Toxicity Chapter | 16 263
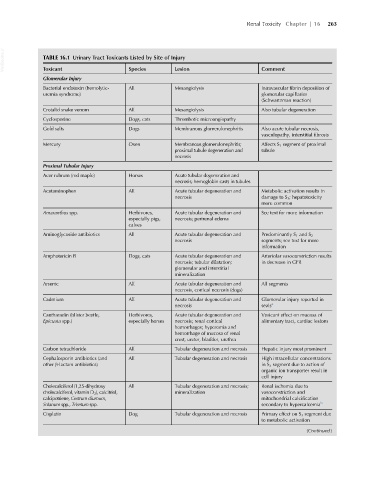
VetBooks.ir TABLE 16.1 Urinary Tract Toxicants Listed by Site of Injury Comment
Lesion
Toxicant
Species
Glomerular Injury
Bacterial endotoxin (hemolytic- All Mesangiolysis Intravascular fibrin deposition of
uremia syndrome) glomerular capillaries
(Schwartzman reaction)
Crotalid snake venom All Mesangiolysis Also tubular degeneration
Cyclosporine Dogs, cats Thrombotic microangiopathy
Gold salts Dogs Membranous glomerulonephritis Also acute tubular necrosis,
vasculopathy, interstitial fibrosis
Mercury Oxen Membranous glomerulonephritis; Affects S 1 segment of proximal
proximal tubule degeneration and tubule
necrosis
Proximal Tubular Injury
Acer rubrum (red maple) Horses Acute tubular degeneration and
necrosis; hemoglobin casts in tubules
Acetaminophen All Acute tubular degeneration and Metabolic activation results in
necrosis damage to S 3 ; hepatotoxicity
more common
Amaranthus spp. Herbivores, Acute tubular degeneration and See text for more information
especially pigs, necrosis; perirenal edema
calves
Aminoglycoside antibiotics All Acute tubular degeneration and Predominantly S 1 and S 2
necrosis segments; see text for more
information
Amphotericin B Dogs, cats Acute tubular degeneration and Arteriolar vasoconstriction results
necrosis; tubular dilatation; in decrease in GFR
glomerular and interstitial
mineralization
Arsenic All Acute tubular degeneration and All segments
necrosis, cortical necrosis (dogs)
Cadmium All Acute tubular degeneration and Glomerular injury reported in
necrosis seals a
Cantharadin (blister beetle, Herbivores, Acute tubular degeneration and Vesicant effect on mucosa of
Epicuata spp.) especially horses necrosis; renal cortical alimentary tract, cardiac lesions
hemorrhages; hyperemia and
hemorrhage of mucosa of renal
crest, ureter, bladder, urethra
Carbon tetrachloride All Tubular degeneration and necrosis Hepatic injury most prominent
Cephalosporin antibiotics (and All Tubular degeneration and necrosis High intracellular concentrations
other β-lactam antibiotics) in S 3 segment due to action of
organic ion transporter result in
cell injury
Cholecalciferol (1,25-dihydroxy All Tubular degeneration and necrosis; Renal ischemia due to
cholecalciferol, vitamin D 3 ), calcitriol, mineralization vasoconstriction and
calcipotriene, Cestrum diurnum, mitochondrial calcification
Solanum spp., Trisetum spp. secondary to hypercalcemia b
Cisplatin Dog Tubular degeneration and necrosis Primary effect on S 3 segment due
to metabolic activation
(Continued )