Page 297 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 297
264 SECTION | II Organ Toxicity
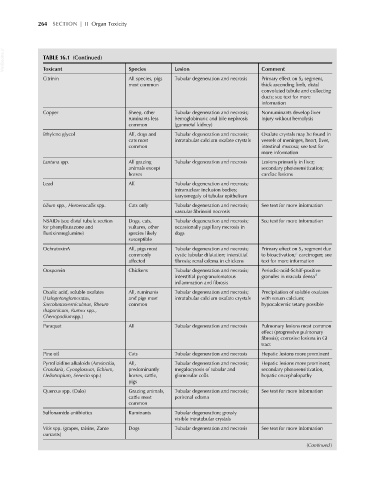
VetBooks.ir TABLE 16.1 (Continued) Species Lesion Comment
Toxicant
Citrinin All species, pigs Tubular degeneration and necrosis Primary effect on S 2 segment,
most common thick ascending limb, distal
convoluted tubule and collecting
ducts; see text for more
information
Copper Sheep, other Tubular degeneration and necrosis; Nonruminants develop liver
ruminants less hemoglobinuric and bile nephrosis injury without hemolysis
common (gunmetal kidney)
Ethylene glycol All, dogs and Tubular degeneration and necrosis; Oxalate crystals may be found in
cats most intratubular calcium oxalate crystals vessels of meninges, heart, liver,
common intestinal mucosa; see text for
more information
Lantana spp. All grazing Tubular degeneration and necrosis Lesions primarily in liver;
animals except secondary photosensitization;
horses cardiac lesions
Lead All Tubular degeneration and necrosis;
intranuclear inclusion bodies;
karyomegaly of tubular epithelium
Lilium spp., Hemerocallis spp. Cats only Tubular degeneration and necrosis; See text for more information
vascular fibrinoid necrosis
NSAIDs (see distal tubule section Dogs, cats, Tubular degeneration and necrosis; See text for more information
for phenylbutazone and vultures, other occasionally papillary necrosis in
flunixinmeglumine) species likely dogs
susceptible
OchratoxinA All, pigs most Tubular degeneration and necrosis; Primary effect on S 3 segment due
c
commonly cystic tubular dilatation; interstitial to bioactivation; carcinogen; see
affected fibrosis; renal edema in chickens text for more information
Oosporein Chickens Tubular degeneration and necrosis; Periodic-acid-Schiff-positive
interstitial pyogranulomatous granules in macula densa d
inflammation and fibrosis
Oxalic acid, soluble oxalates All, ruminants Tubular degeneration and necrosis; Precipitation of soluble oxalates
(Halogetonglomeratus, and pigs most intratubular calcium oxalate crystals with serum calcium;
Sarcobatusverniculatus, Rheum common hypocalcemic tetany possible
rhaponicum, Rumex spp.,
Chenopodiumspp.)
Paraquat All Tubular degeneration and necrosis Pulmonary lesions most common
effect (progressive pulmonary
fibrosis); corrosive lesions in GI
tract
Pine oil Cats Tubular degeneration and necrosis Hepatic lesions more prominent
Pyrrolizidine alkaloids (Amsinckia, All, Tubular degeneration and necrosis; Hepatic lesions more prominent;
Crotolaria, Cynoglossum, Echium, predominantly megalocytosis of tubular and secondary photosensitization,
Heliotropium, Senecio spp.) horses, cattle, glomerular cells hepatic encephalopathy
pigs
Quercus spp. (Oaks) Grazing animals, Tubular degeneration and necrosis; See text for more information
cattle most perirenal edema
common
Sulfonamide antibiotics Ruminants Tubular degeneration; grossly
visible intratubular crystals
Vitis spp. (grapes, raisins, Zante Dogs Tubular degeneration and necrosis See text for more information
currants)
(Continued )