Page 544 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 544
Organochlorines Chapter | 38 511
VetBooks.ir dechlorination and oxidation. The intermediates of OC terminal and inhibition of release of other neurotransmit-
insecticide production may be more toxic than the parent
ters. Because of this inhibition, postsynaptic stimulation
of other nerves by other transmitters (e.g., acetylcholine)
compound.
The major excretory route of OCs is from bile into the is reduced. When GABA is inhibited, there is no synaptic
digestive tract, and as a result enterohepatic recycling can downregulation, and other neurotransmitters can be
occur. Metabolites are also lipophilic, will move into adi- released in excess. The inhibitory mechanism of GABA
pose tissue and are released slowly from lipid depot stor- explains the cholinergic effects (over stimulation by ace-
age (Sell et al., 1977). The half-life of some diphenyl tylcholine) of dieldrin and lindane on some species.
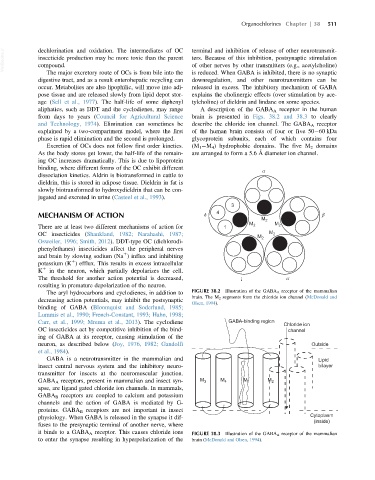
aliphatics, such as DDT and the cyclodienes, may range A description of the GABA A receptor in the human
from days to years (Council for Agricultural Science brain is presented in Figs. 38.2 and 38.3 to clearly
and Technology, 1974). Elimination can sometimes be describe the chloride ion channel. The GABA A receptor
explained by a two-compartment model, where the first of the human brain consists of four or five 50 60 kDa
phase is rapid elimination and the second is prolonged. glycoprotein subunits, each of which contains four
Excretion of OCs does not follow first order kinetics. (M 1 M 4 ) hydrophobic domains. The five M 2 domains
˚
As the body stores get lower, the half-life of the remain- are arranged to form a 5.6 A diameter ion channel.
ing OC increases dramatically. This is due to lipoprotein
binding, where different forms of the OC exhibit different
α
dissociation kinetics. Aldrin is biotransformed in cattle to
dieldrin, this is stored in adipose tissue. Dieldrin in fat is
slowly biotransformed to hydroxydieldrin that can be con-
jugated and excreted in urine (Casteel et al., 1993).
3
MECHANISM OF ACTION δ 4 β
M 2
M M
There are at least two different mechanisms of action for 1 2 2
OC insecticides (Shankland, 1982; Narahashi, 1987; M 2 M 2
Osweiler, 1996; Smith, 2012). DDT-type OC (dichlorodi-
phenylethanes) insecticides affect the peripheral nerves
1
and brain by slowing sodium (Na ) influx and inhibiting
1
potassium (K ) efflux. This results in excess intracellular
1
K in the neuron, which partially depolarizes the cell.
The threshold for another action potential is decreased, ¡ α
resulting in premature depolarization of the neuron.
The aryl hydrocarbons and cyclodienes, in addition to FIGURE 38.2 Illustration of the GABA A receptor of the mammalian
brain. The M 2 segments form the chloride ion channel (McDonald and
decreasing action potentials, may inhibit the postsynaptic
Olsen, 1994).
binding of GABA (Bloomquist and Soderlund, 1985;
Lummis et al., 1990; French-Constant, 1993; Hahn, 1998;
Carr, et al., 1999; Mrema et al., 2013). The cyclodiene GABA-binding region
Chloride ion
OC insecticides act by competitive inhibition of the bind- channel
ing of GABA at its receptor, causing stimulation of the
neuron, as described below (Joy, 1976, 1982; Gandolfi Outside
et al., 1984).
GABA is a neurotransmitter in the mammalian and Lipid
insect central nervous system and the inhibitory neuro- bilayer
transmitter for insects at the neuromuscular junction.
GABA A receptors, present in mammalian and insect syn- M 3 M 4 M 1 M 2
apse, are ligand gated chloride ion channels. In mammals,
GABA B receptors are coupled to calcium and potassium
channels and the action of GABA is mediated by G-
proteins. GABA B receptors are not important in insect
physiology. When GABA is released in the synapse it dif- Cytoplasm
(inside)
fuses to the presynaptic terminal of another nerve, where
it binds to a GABA A receptor. This causes chloride ions FIGURE 38.3 Illustration of the GABA A receptor of the mammalian
to enter the synapse resulting in hyperpolarization of the brain (McDonald and Olsen, 1994).