Page 555 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 555
522 SECTION | VI Insecticides
VetBooks.ir CI N NO 2 imidacloprid in rats has been demonstrated at doses above
300 mg/kg with 100% mortality at 500 mg/kg. At doses
in rats above 300 mg/kg, clinical signs were observed
N within 15 min of dosing and recovery was observed
H C within 8 24 h. A subchronic 13-week oral dosing study
2
N of imidacloprid in rats also demonstrated toxicity at a
N H
dose of 300 mg/kg in male rats. At a dose of 300 mg/kg
in male rats, hypertrophy of hepatocytes and sporadic cell
necrosis was observed in the liver. This mild liver damage
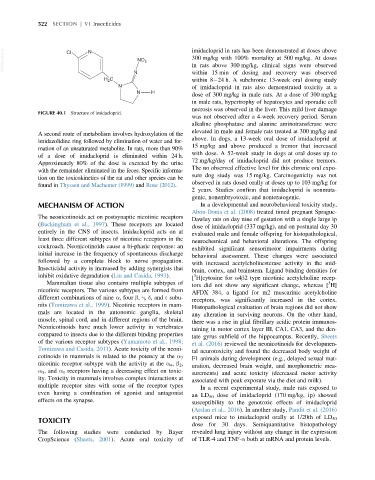
FIGURE 40.1 Structure of imidacloprid.
was not observed after a 4-week recovery period. Serum
alkaline phosphatase and alanine aminotransferase were
elevated in male and female rats treated at 300 mg/kg and
A second route of metabolism involves hydroxylation of the
above. In dogs, a 13-week oral dose of imidacloprid at
imidazolidine ring followed by elimination of water and for-
15 mg/kg and above produced a tremor that increased
mation of an unsaturated metabolite. In rats, more than 90%
with dose. A 52-week study in dogs at oral doses up to
of a dose of imidacloprid is eliminated within 24 h.
72 mg/kg/day of imidacloprid did not produce tremors.
Approximately 80% of the dose is excreted by the urine
The no observed effective level for this chronic oral expo-
with the remainder eliminated in the feces. Specific informa-
sure dog study was 15 mg/kg. Carcinogenicity was not
tion on the toxicokinetics of the rat and other species can be
observed in rats dosed orally at doses up to 103 mg/kg for
found in Thyssen and Machemer (1999) and Rose (2012).
2 years. Studies confirm that imidacloprid is nonmuta-
genic, nonembryotoxic, and nonteratogenic.
MECHANISM OF ACTION In a developmental and neurobehavioral toxicity study,
Abou-Donia et al. (2008) treated timed pregnant Sprague-
The neonicotinoids act on postsynaptic nicotinic receptors
Dawley rats on day nine of gestation with a single large ip
(Buckingham et al., 1997). These receptors are located
dose of imidacloprid (337 mg/kg), and on postnatal day 30
entirely in the CNS of insects. Imidacloprid acts on at
evaluated male and female offspring for histopathological,
least three different subtypes of nicotinic receptors in the neurochemical and behavioral alterations. The offspring
cockroach. Neonicotinoids cause a bi-phasic response: an exhibited significant sensorimotor impairments during
initial increase in the frequency of spontaneous discharge behavioral assessment. These changes were associated
followed by a complete block to nerve propagation. with increased acetylcholinesterase activity in the mid-
Insecticidal activity is increased by adding synergists that brain, cortex, and brainstem. Ligand binding densities for
inhibit oxidative degradation (Liu and Casida, 1993). [ H]cytosine for α4β2 type nicotinic acetylcholine recep-
3
Mammalian tissue also contains multiple subtypes of tors did not show any significant change, whereas [ H]
3
nicotinic receptors. The various subtypes are formed from
AFDX 384, a ligand for m2 muscarinic acetylcholine
different combinations of nine α, four β, γ, δ, and ε subu-
receptors, was significantly increased in the cortex.
nits (Tomizawa et al., 1999). Nicotinic receptors in mam-
Histopathological evaluation of brain regions did not show
mals are located in the autonomic ganglia, skeletal
any alteration in surviving neurons. On the other hand,
muscle, spinal cord, and in different regions of the brain.
there was a rise in glial fibrillary acidic protein immunos-
Neonicotinoids have much lower activity in vertebrates
taining in motor cortex layer III, CA1, CA3, and the den-
compared to insects due to the different binding properties
tate gyrus subfield of the hippocampus. Recently, Sheets
of the various receptor subtypes (Yamamoto et al., 1998;
et al. (2016) reviewed the neonicotinoids for developmen-
Tomizawa and Casida, 2011). Acute toxicity of the neoni-
tal neurotoxicity and found the decreased body weight of
F1 animals during development (e.g., delayed sexual mat-
cotinoids in mammals is related to the potency at the α 7
nicotinic receptor subtype with the activity at the α 4 , β 2 ,
uration, decreased brain weight, and morphometric mea-
α 3 , and α 1 receptors having a decreasing effect on toxic-
surements) and acute toxicity (decreased motor activity
ity. Toxicity in mammals involves complex interactions at
associated with peak exposure via the diet and milk).
multiple receptor sites with some of the receptor types
In a recent experimental study, male rats exposed to
even having a combination of agonist and antagonist
an LD 50 dose of imidacloprid (170 mg/kg, ip) showed
effects on the synapse. susceptibility to the genotoxic effects of imidacloprid
(Arslan et al., 2016). In another study, Pandit et al. (2016)
TOXICITY exposed mice to imidacloprid orally at 1/20th of LD 50
dose for 30 days. Semiquantitative histopathology
The following studies were conducted by Bayer revealed lung injury without any change in the expression
CropScience (Sheets, 2001). Acute oral toxicity of of TLR-4 and TNF-α both at mRNA and protein levels.