Page 593 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 593
558 SECTION | VII Herbicides and Fungicides
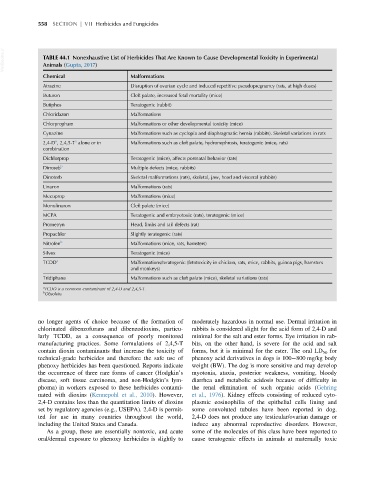
VetBooks.ir TABLE 44.1 Nonexhaustive List of Herbicides That Are Known to Cause Developmental Toxicity in Experimental
Animals (Gupta, 2017)
Chemical Malformations
Atrazine Disruption of ovarian cycle and induced repetitive pseudopregnancy (rats, at high doses)
Buturon Cleft palate, increased fetal mortality (mice)
Butiphos Teratogenic (rabbit)
Chloridazon Malformations
Chlorpropham Malformations or other developmental toxicity (mice)
Cynazine Malformations such as cyclopia and diaphragmatic hernia (rabbits). Skeletal variations in rats
a
a
2,4-D , 2,4,5-T alone or in Malformations such as cleft palate, hydronephrosis, teratogenic (mice, rats)
combination
Dichlorprop Teratogenic (mice), affects postnatal behavior (rats)
Dinoseb b Multiple defects (mice, rabbits)
Dinoterb Skeletal malformations (rats), skeletal, jaw, head and visceral (rabbits)
Linuron Malformations (rats)
Mecoprop Malformations (mice)
Monolinuron Cleft palate (mice)
MCPA Teratogenic and embryotoxic (rats), teratogenic (mice)
Prometryn Head, limbs and tail defects (rat)
Propachlor Slightly teratogenic (rats)
Nitrofen b Malformations (mice, rats, hamsters)
Silvex Teratogenic (mice)
TCDD a Malformations/teratogenic (fetotoxicity in chicken, rats, mice, rabbits, guinea pigs, hamsters
and monkeys)
Tridiphane Malformations such as cleft palate (mice), skeletal variations (rats)
a
TCDD is a common contaminant of 2,4-D and 2,4,5-T.
b
Obsolete.
no longer agents of choice because of the formation of moderately hazardous in normal use. Dermal irritation in
chlorinated dibenzofurans and dibenzodioxins, particu- rabbits is considered slight for the acid form of 2,4-D and
larly TCDD, as a consequence of poorly monitored minimal for the salt and ester forms. Eye irritation in rab-
manufacturing practices. Some formulations of 2,4,5-T bits, on the other hand, is severe for the acid and salt
contain dioxin contaminants that increase the toxicity of forms, but it is minimal for the ester. The oral LD 50 for
technical-grade herbicides and therefore the safe use of phenoxy acid derivatives in dogs is 100 800 mg/kg body
phenoxy herbicides has been questioned. Reports indicate weight (BW). The dog is more sensitive and may develop
the occurrence of three rare forms of cancer (Hodgkin’s myotonia, ataxia, posterior weakness, vomiting, bloody
disease, soft tissue carcinoma, and non-Hodgkin’s lym- diarrhea and metabolic acidosis because of difficulty in
phoma) in workers exposed to these herbicides contami- the renal elimination of such organic acids (Gehring
nated with dioxins (Kennepohl et al., 2010). However, et al., 1976). Kidney effects consisting of reduced cyto-
2,4-D contains less than the quantitation limits of dioxins plasmic eosinophilia of the epithelial cells lining and
set by regulatory agencies (e.g., USEPA). 2,4-D is permit- some convoluted tubules have been reported in dog.
ted for use in many countries throughout the world, 2,4-D does not produce any testicular/ovarian damage or
including the United States and Canada. induce any abnormal reproductive disorders. However,
As a group, these are essentially nontoxic, and acute some of the molecules of this class have been reported to
oral/dermal exposure to phenoxy herbicides is slightly to cause teratogenic effects in animals at maternally toxic