Page 650 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 650
Non-Anticoagulant Rodenticides Chapter | 47 615
VetBooks.ir GC mass spectrometry (GC-MS). It is important to note Background
that strychnine causes elevation of serum enzymes, includ-
Bromethalin was developed for use against warfarin-
ing glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, creatine phosphoki-
nase, and lactate dehydrogenase. In addition, lactic resistant rodents. It is a restricted-use rodenticide used in
and around buildings and sewers and inside transporta-
acidosis, hyperkalemia, and leukocytosis are the character-
tion and cargo vehicles. It is extremely toxic, and only a
istic laboratory findings. In differential diagnosis, tetanus
single dose of bromethalin is needed to cause death in
must be ruled out.
rats and mice. Bromethalin is marketed in a 0.01% for-
mulation (2.84 mg of bromethalin per ounce of bait), and
Treatment comes in bait pellets, bars, and packs. It is important to
note that bromethalin cannot be distinguished from other
There is no specific antidote for strychnine poisoning, so
rodent baits by color or appearance alone. Secondary poi-
treatment rests with symptomatic and supportive thera-
soning usually occurs in dogs and cats that eat a mouse
pies. Seizures need to be controlled as soon as possible
killed by bromethalin. There are few cases of brometha-
with diazepam or phenobarbital. Artificial respiration can
lin poisoning in humans following accidental exposure or
be used for apnea. Once the seizures are controlled,
suicidal intent (Pasquale-Styles et al., 2006; Huntington
detoxification can be performed using gastric lavage with
et al., 2016).
potassium permanganate. Give activated charcoal with a
saline cathartic to stop further absorption in the GI tract.
Animals should be kept in a quiet environment and pro- Toxicokinetics
tected from any secondary sensory input.
Toxicokinetic information on bromethalin is available from
laboratory animals such as rats. Bromethalin is rapidly
Conclusion absorbed following oral ingestion. Plasma concentration
peaks in approximately 4 h. Metabolism takes place in the
Strychnine is an extremely toxic plant alkaloid that is pri-
liver, where bromethalin undergoes N-demethylation,
marily used as rodenticide. Due to inadvertent use or
forming desmethyl bromethalin. This metabolite is toxic,
malicious intent, the poisoning is frequently encountered
as its LD 50 is 7.5 mg/kg body weight. The plasma half-life
in dogs. Onset of clinical signs occurs very quickly, and
of bromethalin is approximately 6 days (Dorman et al.,
the poisoning is characterized by convulsions, seizures, 1990c), suggesting slow elimination. Excretion occurs
and hypersensitivity to any external stimulus. Treatment mainly in bile, as it enters into enterohepatic circulation.
is symptomatic, and warranted immediately.
Mechanism of Action
BROMETHALIN
Bromethalin is a neurotoxicant, and affects the CNS. It
Introduction uncouples oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria,
thereby decreasing ATP synthesis. With a marked deple-
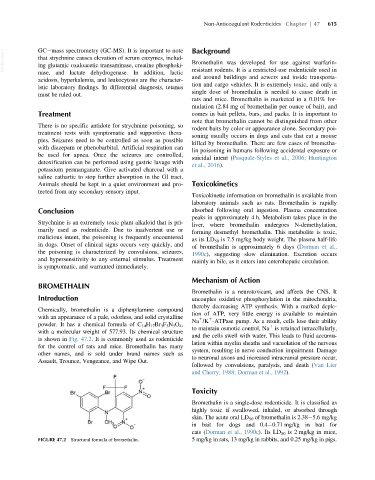
Chemically, bromethalin is a diphenylamine compound
tion of ATP, very little energy is available to maintain
with an appearance of a pale, odorless, and solid crystalline 1 1
Na /K -ATPase pump. As a result, cells lose their ability
powder. It has a chemical formula of C 14 H 17 Br 3 F 3 N 3 O 4 , 1
to maintain osmotic control, Na is retained intracellularly,
with a molecular weight of 577.93. Its chemical structure
and the cells swell with water. This leads to fluid accumu-
is shown in Fig. 47.2. It is commonly used as rodenticide
lation within myelin sheaths and vacuolation of the nervous
for the control of rats and mice. Bromethalin has many
system, resulting in nerve conduction impairment. Damage
other names, and is sold under brand names such as
to neuronal axons and increased intracranial pressure occur,
Assault, Trounce, Vengeance, and Wipe Out.
followed by convulsions, paralysis, and death (Van Lier
and Cherry, 1988; Dorman et al., 1992).
Toxicity
Bromethalin is a single-dose rodenticide. It is classified as
highly toxic if swallowed, inhaled, or absorbed through
skin. The acute oral LD 50 of bromethalin is 2.38 5.6 mg/kg
in bait for dogs and 0.4 0.71 mg/kg in bait for
cats (Dorman et al., 1990c). Its LD 50 is 2 mg/kg in mice,
FIGURE 47.2 Structural formula of bromethalin. 5 mg/kg in rats, 13 mg/kg in rabbits, and 0.25 mg/kg in pigs.