Page 75 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 75
42 SECTION | I General
VetBooks.ir
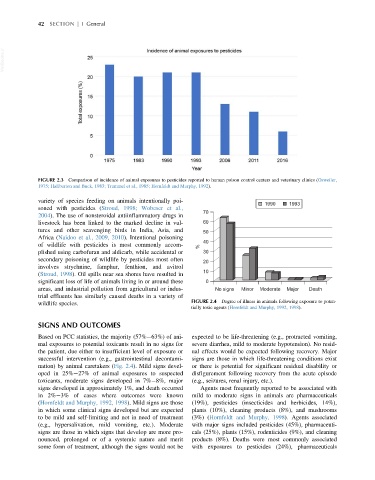
FIGURE 2.3 Comparison of incidence of animal exposures to pesticides reported to human poison control centers and veterinary clinics (Osweiler,
1975; Haliburton and Buck, 1983; Trammel et al., 1985; Hornfeldt and Murphy, 1992).
variety of species feeding on animals intentionally poi-
1990 1993
soned with pesticides (Stroud, 1998; Wobeser et al.,
70
2004). The use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs in
livestock has been linked to the marked decline in vul- 60
tures and other scavenging birds in India, Asia, and 50
Africa (Naidoo et al., 2009, 2010). Intentional poisoning
40
of wildlife with pesticides is most commonly accom-
%
plished using carbofuran and aldicarb, while accidental or 30
secondary poisoning of wildlife by pesticides most often
20
involves strychnine, famphur, fenthion, and avitrol
(Stroud, 1998). Oil spills near sea shores have resulted in 10
significant loss of life of animals living in or around these 0
areas, and industrial pollution from agricultural or indus- No signs Minor Moderate Major Death
trial effluents has similarly caused deaths in a variety of
wildlife species. FIGURE 2.4 Degree of illness in animals following exposure to poten-
tially toxic agents (Hornfeldt and Murphy, 1992, 1998).
SIGNS AND OUTCOMES
Based on PCC statistics, the majority (57% 63%) of ani- expected to be life-threatening (e.g., protracted vomiting,
mal exposures to potential toxicants result in no signs for severe diarrhea, mild to moderate hypotension). No resid-
the patient, due either to insufficient level of exposure or ual effects would be expected following recovery. Major
successful intervention (e.g., gastrointestinal decontami- signs are those in which life-threatening conditions exist
nation) by animal caretakers (Fig. 2.4). Mild signs devel- or there is potential for significant residual disability or
oped in 25% 27% of animal exposures to suspected disfigurement following recovery from the acute episode
toxicants, moderate signs developed in 7% 8%, major (e.g., seizures, renal injury, etc.).
signs developed in approximately 1%, and death occurred Agents most frequently reported to be associated with
in 2% 3% of cases where outcomes were known mild to moderate signs in animals are pharmaceuticals
(Hornfeldt and Murphy, 1992, 1998). Mild signs are those (19%), pesticides (insecticides and herbicides, 14%),
in which some clinical signs developed but are expected plants (10%), cleaning products (8%), and mushrooms
to be mild and self-limiting and not in need of treatment (3%) (Hornfeldt and Murphy, 1998). Agents associated
(e.g., hypersalivation, mild vomiting, etc.). Moderate with major signs included pesticides (45%), pharmaceuti-
signs are those in which signs that develop are more pro- cals (25%), plants (15%), rodenticides (9%), and cleaning
nounced, prolonged or of a systemic nature and merit products (8%). Deaths were most commonly associated
some form of treatment, although the signs would not be with exposures to pesticides (24%), pharmaceuticals