Page 80 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 80
Epidemiology of Animal Poisonings in Europe Chapter | 3 47
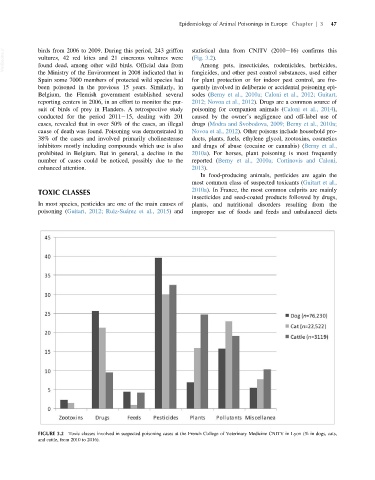
VetBooks.ir birds from 2006 to 2009. During this period, 243 griffon statistical data from CNITV (2010 16) confirms this
(Fig. 3.2).
vultures, 42 red kites and 21 cinereous vultures were
Among pets, insecticides, rodenticides, herbicides,
found dead, among other wild birds. Official data from
the Ministry of the Environment in 2008 indicated that in fungicides, and other pest control substances, used either
Spain some 7000 members of protected wild species had for plant protection or for indoor pest control, are fre-
been poisoned in the previous 15 years. Similarly, in quently involved in deliberate or accidental poisoning epi-
Belgium, the Flemish government established several sodes (Berny et al., 2010a; Caloni et al., 2012; Guitart,
reporting centers in 2006, in an effort to monitor the pur- 2012; Novoa et al., 2012). Drugs are a common source of
suit of birds of prey in Flanders. A retrospective study poisoning for companion animals (Caloni et al., 2014),
conducted for the period 2011 15, dealing with 201 caused by the owner’s negligence and off-label use of
cases, revealed that in over 50% of the cases, an illegal drugs (Modra and Svobodova, 2009; Berny et al., 2010a;
cause of death was found. Poisoning was demonstrated in Novoa et al., 2012). Other poisons include household pro-
38% of the cases and involved primarily cholinesterase ducts, plants, fuels, ethylene glycol, zootoxins, cosmetics
inhibitors mostly including compounds which use is also and drugs of abuse (cocaine or cannabis) (Berny et al.,
prohibited in Belgium. But in general, a decline in the 2010a). For horses, plant poisoning is most frequently
number of cases could be noticed, possibly due to the reported (Berny et al., 2010a; Cortinovis and Caloni,
enhanced attention. 2013).
In food-producing animals, pesticides are again the
most common class of suspected toxicants (Guitart et al.,
TOXIC CLASSES 2010a). In France, the most common culprits are mainly
insecticides and seed-coated products followed by drugs,
In most species, pesticides are one of the main causes of plants, and nutritional disorders resulting from the
poisoning (Guitart, 2012; Ruiz-Sua ´rez et al., 2015) and improper use of foods and feeds and unbalanced diets
FIGURE 3.2 Toxic classes involved in suspected poisoning cases at the French College of Veterinary Medicine CNITV in Lyon (% in dogs, cats,
and cattle, from 2010 to 2016).