Page 763 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 763
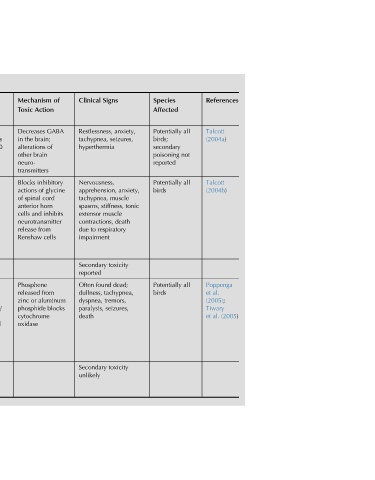
References Talcott (2004a) Talcott (2004b) Poppenga al. et (2005); Tiwary (2005) al. et
all not all all
Species Affected Potentially birds; secondary poisoning reported Potentially birds Potentially birds
anxiety, seizures, anxiety, muscle tonic death toxicity dead; tachypnea, toxicity
Signs stiffness, muscle respiratory found tremors, seizures,
Clinical Restlessness, tachypnea, hyperthermia Nervousness, apprehension, tachypnea, spasms, extensor contractions, to due impairment Secondary reported Often dullness, dyspnea, paralysis, death Secondary unlikely
of GABA of inhibitory glycine cord horn inhibits cells from aluminum blocks
Mechanism Action Toxic Decreases brain; the in alterations brain other neuro- transmitters Blocks of actions spinal of anterior and cells neurotransmitter from release Renshaw Phosphene released or zinc phosphide cytochrome oxidase
Toxicity lethal chickens for 500 are ducks mg/kg respectively oral golden for sage and are and 42.5, mg/kg, for LD 50 s and birds to reported mg/ 23.7 37.5 in LD 50 reported mg/kg 25
Avian Minimum doses and 300 and BW, Reported LD 50 s eagles, grouse, pheasants 5 10, 8.5 24.7 respectively Oral wild ducks be oral kg; chickens be to
granules, powders baits grain-based sulfate scrap bait, tracking generally zinc 0.5% 2.0% to up paste
Formulations baits, Pelleted or liquids, wettable 5% containing metaldehyde Colored 0.5% 1.0% with strychnine Grain-based or paste, bait, baits powder; contain phosphide; 10%
slugs snails Controlling squirrels, and meadow mice, dogs, porcupines, chipmunks, control to mice, ground squirrels, dogs, muskrats, opossums, Aluminum phosphide a as fumigant
(Continued) Uses Control and ground deer prairie rabbits, pigeons Used rats, voles, prairie nutrias, rabbits, gophers used
53.2 Rodenticides/ Molluscicides phosphide
TABLE Avicides/ Metaldehyde Strychnine Zinc
VetBooks.ir