Page 704 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 704
676 PART V Urinary Tract Disorders
Capillary endothelium
Afferent Glomerular Podocyte
VetBooks.ir Juxtaglomerular membrane Endothelial cell
arteriole
basement
Fenestrated
Macula cells Proximal endothelium
tubule
Basement
densa
membrane of
Distal endothelium
tubule Podocyte feet
Mesangial cell
Intercellular
Bowman’s substance
space
Efferent Basement
arteriole Parietal epithelium membrane
Visceral epithelium of epithelium
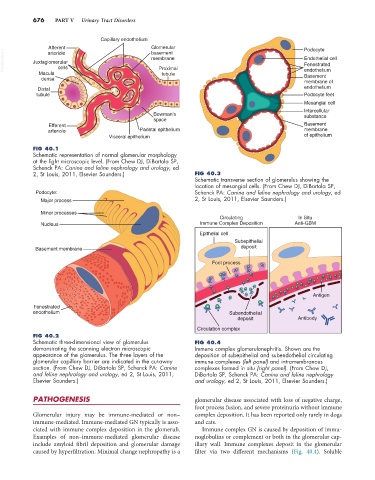
FIG 40.1
Schematic representation of normal glomerular morphology
at the light microscopic level. (From Chew DJ, DiBartola SP,
Schenck PA: Canine and feline nephrology and urology, ed
2, St Louis, 2011, Elsevier Saunders.) FIG 40.3
Schematic transverse section of glomerulus showing the
location of mesangial cells. (From Chew DJ, DiBartola SP,
Podocyte: Schenck PA: Canine and feline nephrology and urology, ed
Major process 2, St Louis, 2011, Elsevier Saunders.)
Minor processes
Circulating In Situ
Nucleus Immune Complex Deposition Anti-GBM
Epithelial cell
Subepithelial
Basement membrane deposit
Foot process
Antigen
Fenestrated
endothelium Subendothelial
deposit Antibody
Circulation complex
FIG 40.2
Schematic three-dimensional view of glomerulus FIG 40.4
demonstrating the scanning electron microscopic Immune complex glomerulonephritis. Shown are the
appearance of the glomerulus. The three layers of the deposition of subepithelial and subendothelial circulating
glomerular capillary barrier are indicated in the cut-away immune complexes (left panel) and intramembranous
section. (From Chew DJ, DiBartola SP, Schenck PA: Canine complexes formed in situ (right panel). (From Chew DJ,
and feline nephrology and urology, ed 2, St Louis, 2011, DiBartola SP, Schenck PA: Canine and feline nephrology
Elsevier Saunders.) and urology, ed 2, St Louis, 2011, Elsevier Saunders.)
PATHOGENESIS glomerular disease associated with loss of negative charge,
foot process fusion, and severe proteinuria without immune
Glomerular injury may be immune-mediated or non– complex deposition. It has been reported only rarely in dogs
immune-mediated. Immune-mediated GN typically is asso- and cats.
ciated with immune complex deposition in the glomeruli. Immune complex GN is caused by deposition of immu-
Examples of non–immune-mediated glomerular disease noglobulins or complement or both in the glomerular cap-
include amyloid fibril deposition and glomerular damage illary wall. Immune complexes deposit in the glomerular
caused by hyperfiltration. Minimal change nephropathy is a filter via two different mechanisms (Fig. 40.4). Soluble