Page 748 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 748
720 PART V Urinary Tract Disorders
Dietary and enendogenous purines BOX 43.3
VetBooks.ir Hypoxanthine Management of Canine Urate Urolithiasis for Dogs With
Genetic Hyperuricosuria
Xanthine oxidase
1. Can attempt urate urolith dissolution if urinary
obstruction not present with a low-protein or low-
Xanthine purine diet and allopurinol. If unsuccessful, remove all
Xanthine oxidase uroliths and confirm via ultrasonography or contrast
radiography.
Uric acid 2. Submit all uroliths for quantitative analysis as well as
Uricase infrared spectroscopy, which are required to
differentiate uric acid from its metabolites.
Allantoin Urine 3. Select a diet appropriate for the dog, and consider all
comorbid conditions that may be present. Diets
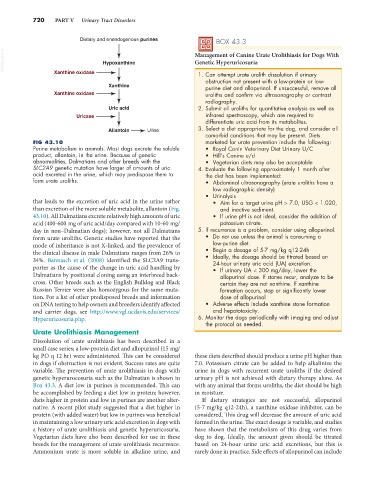
FIG 43.10 marketed for urate prevention include the following:
Purine metabolism in animals. Most dogs excrete the soluble • Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Urinary U/C
product, allantoin, in the urine. Because of genetic • Hill’s Canine u/d
abnormalities, Dalmatians and other breeds with the • Vegetarian diets may also be acceptable
SLC2A9 genetic mutation have larger of amounts of uric 4. Evaluate the following approximately 1 month after
acid excreted in the urine, which may predispose them to the diet has been implemented:
form urate uroliths. • Abdominal ultrasonography (urate uroliths have a
low radiographic density)
• Urinalysis
that leads to the excretion of uric acid in the urine rather • Aim for a target urine pH > 7.0, USG < 1.020,
than excretion of the more soluble metabolite, allantoin (Fig. and inactive sediment.
43.10). All Dalmatians excrete relatively high amounts of uric • If urine pH is not ideal, consider the addition of
acid (400-600 mg of uric acid/day compared with 10-60 mg/ potassium citrate.
day in non–Dalmatian dogs); however, not all Dalmatians 5. If recurrence is a problem, consider using allopurinol.
form urate uroliths. Genetic studies have reported that the • Do not use unless the animal is consuming a
mode of inheritance is not X-linked, and the prevalence of low-purine diet.
the clinical disease in male Dalmatians ranges from 26% to • Begin a dosage of 5-7 mg/kg q12-24h
• Ideally, the dosage should be titrated based on
34%. Bannasch et al. (2008) identified the SLC2A9 trans- 24-hour urinary uric acid (UA) excretion.
porter as the cause of the change in uric acid handling by • If urinary UA < 300 mg/day, lower the
Dalmatians by positional cloning using an interbreed back- allopurinol dose. If stones recur, analyze to be
cross. Other breeds such as the English Bulldog and Black certain they are not xanthine. If xanthine
Russian Terrier were also homozygous for the same muta- formation occurs, stop or significantly lower
tion. For a list of other predisposed breeds and information dose of allopurinol
on DNA testing to help owners and breeders identify affected • Adverse effects include xanthine stone formation
and carrier dogs, see http://www.vgl.ucdavis.edu/services/ and hepatotoxicity.
Hyperuricosuria.php. 6. Monitor the dogs periodically with imaging and adjust
the protocol as needed.
Urate Urolithiasis Management
Dissolution of urate urolithiasis has been described in a
small case series; a low-protein diet and allopurinol (15 mg/
kg PO q 12 hr) were administered. This can be considered these diets described should produce a urine pH higher than
in dogs if obstruction is not evident. Success rates are quite 7.0. Potassium citrate can be added to help alkalinize the
variable. The prevention of urate urolithiasis in dogs with urine in dogs with recurrent urate uroliths if the desired
genetic hyperurocosuria such as the Dalmatian is shown in urinary pH is not achieved with dietary therapy alone. As
Box 43.3. A diet low in purines is recommended. This can with any animal that forms uroliths, the diet should be high
be accomplished by feeding a diet low in protein; however, in moisture.
diets higher in protein and low in purines are another alter- If dietary strategies are not successful, allopurinol
native. A recent pilot study suggested that a diet higher in (5-7 mg/kg q12-24h), a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, can be
protein (with added water) but low in purines was beneficial considered. This drug will decrease the amount of uric acid
in maintaining a low urinary uric acid excretion in dogs with formed in the urine. The exact dosage is variable, and studies
a history of urate urolithiasis and genetic hyperuricosuria. have shown that the metabolism of this drug varies from
Vegetarian diets have also been described for use in these dog to dog. Ideally, the amount given should be titrated
breeds for the management of urate urolithiasis recurrence. based on 24-hour urine uric acid excretions, but this is
Ammonium urate is more soluble in alkaline urine, and rarely done in practice. Side effects of allopurinol can include