Page 809 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 809
CHAPTER 48 Disorders of the Thyroid Gland 781
glucocorticoid, dosage, route of administration, and dura-
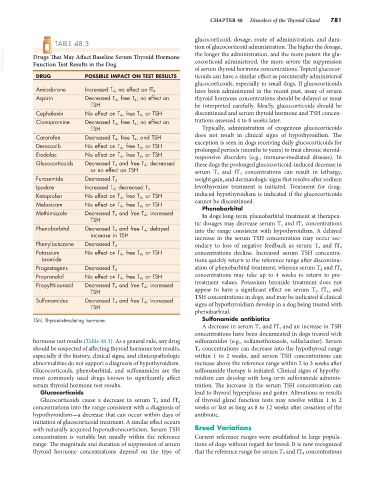
TABLE 48.3 tion of glucocorticoid administration. The higher the dosage,
VetBooks.ir Drugs That May Affect Baseline Serum Thyroid Hormone the longer the administration, and the more potent the glu-
cocorticoid administered, the more severe the suppression
Function Test Results in the Dog
ticoids can have a similar effect as parenterally administered
DRUG POSSIBLE IMPACT ON TEST RESULTS of serum thyroid hormone concentrations. Topical glucocor-
glucocorticoids, especially in small dogs. If glucocorticoids
Amiodarone Increased T 4 ; no effect on fT 4 have been administered in the recent past, assay of serum
Aspirin Decreased T 4, free T 4; no effect on thyroid hormone concentrations should be delayed or must
TSH be interpreted carefully. Ideally, glucocorticoids should be
Cephalexin No effect on T 4 , free T 4 , or TSH discontinued and serum thyroid hormone and TSH concen-
Clomipramine Decreased T 4, free T 4; no effect on trations assessed 4 to 8 weeks later.
TSH Typically, administration of exogenous glucocorticoids
Carprofen Decreased T 4, free T 4, and TSH does not result in clinical signs of hypothyroidism. The
Deracoxib No effect on T 4 , free T 4 , or TSH exception is seen in dogs receiving daily glucocorticoids for
prolonged periods (months to years) to treat chronic steroid-
Etodolac No effect on T 4, free T 4, or TSH responsive disorders (e.g., immune-mediated disease). In
Glucocorticoids Decreased T 4 and free T 4 ; decreased these dogs the prolonged glucocorticoid-induced decrease in
or no effect on TSH serum T 4 and fT 4 concentrations can result in lethargy,
Furosemide Decreased T 4 weight gain, and dermatologic signs that resolve after sodium
Ipodate Increased T 4; decreased T 3 levothyroxine treatment is initiated. Treatment for drug-
Ketoprofen No effect on T 4 , free T 4 , or TSH induced hypothyroidism is indicated if the glucocorticoids
Meloxicam No effect on T 4 , free T 4, or TSH cannot be discontinued.
Phenobarbital
Methimazole Decreased T 4 and free T 4 ; increased In dogs long-term phenobarbital treatment at therapeu-
TSH tic dosages may decrease serum T 4 and fT 4 concentrations
Phenobarbital Decreased T 4 and free T 4; delayed into the range consistent with hypothyroidism. A delayed
increase in TSH increase in the serum TSH concentration may occur sec-
Phenylbutazone Decreased T 4 ondary to loss of negative feedback as serum T 4 and fT 4
Potassium No effect on T 4 , free T 4 , or TSH concentrations decline. Increased serum TSH concentra-
bromide tions quickly return to the reference range after discontinu-
Progestagens Decreased T 4 ation of phenobarbital treatment, whereas serum T 4 and fT 4
Propranolol No effect on T 4 , free T 4, or TSH concentrations may take up to 4 weeks to return to pre-
Propylthiouracil Decreased T 4 and free T 4 ; increased treatment values. Potassium bromide treatment does not
TSH appear to have a significant effect on serum T 4 , fT 4 , and
Sulfonamides Decreased T 4 and free T 4 ; increased TSH concentrations in dogs, and may be indicated if clinical
TSH signs of hypothyroidism develop in a dog being treated with
phenobarbital.
TSH, Thyroid-stimulating hormone. Sulfonamide antibiotics
A decrease in serum T 4 and fT 4 and an increase in TSH
concentrations have been documented in dogs treated with
hormone test results (Table 48.3). As a general rule, any drug sulfonamides (e.g., sulfamethoxazole, sulfadiazine). Serum
should be suspected of affecting thyroid hormone test results, T 4 concentrations can decrease into the hypothyroid range
especially if the history, clinical signs, and clinicopathologic within 1 to 2 weeks, and serum TSH concentrations can
abnormalities do not support a diagnosis of hypothyroidism. increase above the reference range within 2 to 3 weeks after
Glucocorticoids, phenobarbital, and sulfonamides are the sulfonamide therapy is initiated. Clinical signs of hypothy-
most commonly used drugs known to significantly affect roidism can develop with long-term sulfonamide adminis-
serum thyroid hormone test results. tration. The increase in the serum TSH concentration can
Glucocorticoids lead to thyroid hyperplasia and goiter. Alterations in results
Glucocorticoids cause a decrease in serum T 4 and fT 4 of thyroid gland function tests may resolve within 1 to 2
concentrations into the range consistent with a diagnosis of weeks or last as long as 8 to 12 weeks after cessation of the
hypothyroidism—a decrease that can occur within days of antibiotic.
initiation of glucocorticoid treatment. A similar effect occurs
with naturally acquired hyperadrenocorticism. Serum TSH Breed Variations
concentration is variable but usually within the reference Current reference ranges were established in large popula-
range. The magnitude and duration of suppression of serum tions of dogs without regard for breed. It is now recognized
thyroid hormone concentrations depend on the type of that the reference range for serum T 4 and fT 4 concentrations