Page 804 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 804
776 PART VI Endocrine Disorders
1.6 BOX 48.4
VetBooks.ir Diagnostic Tests for Evaluating Thyroid Gland Function
in the Dog
The decision to assess thyroid gland function should be
based on results of the history, physical examination, and
1.2
routine blood work (complete blood count, serum biochem-
istry panel, urinalysis).
Serum T 3 concentration (ng/mL) 0.8 Exception: T 4 autoantibodies that interfere with T 4 assay
Serum Thyroxine (T 4 )
This is the most commonly used initial screening test for
hypothyroidism.
Normal serum T 4 rules out hypothyroidism.
and cause spuriously high results (uncommon).
Low serum T 4 does not, by itself, confirm hypothyroidism.
Serum T 4 is commonly suppressed below the reference
range by nonthyroidal illness, drugs, and other factors
in dogs with normal thyroid gland function.
0.4
Serum Free Thyroxine (fT 4 )
This is usually measured in dogs with nondiagnostic
serum T 4 test results, severe nonthyroidal illness, or
both, and is a common component of canine thyroid
panels.
Normal serum fT 4 rules out hypothyroidism.
0
Low serum fT 4 does not, by itself, confirm hypothyroidism;
Healthy Hypothyroid Euthyroid dogs severe nonthyroidal illness and drugs can suppress
dogs dogs with dermatopathy serum fT 4 to below the reference range.
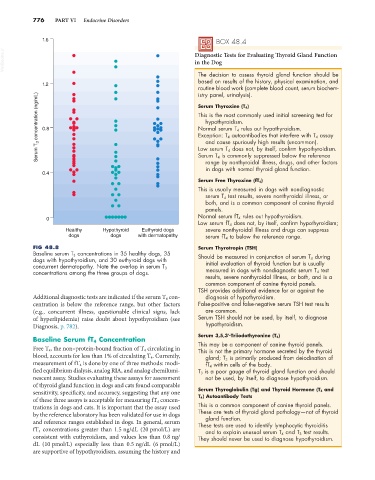
FIG 48.8 Serum Thyrotropin (TSH)
Baseline serum T 3 concentrations in 35 healthy dogs, 35 Should be measured in conjunction of serum T 4 during
dogs with hypothyroidism, and 30 euthyroid dogs with
concurrent dermatopathy. Note the overlap in serum T 3 initial evaluation of thyroid function but is usually
concentrations among the three groups of dogs. measured in dogs with nondiagnostic serum T 4 test
results, severe nonthyroidal illness, or both, and is a
common component of canine thyroid panels.
TSH provides additional evidence for or against the
Additional diagnostic tests are indicated if the serum T 4 con- diagnosis of hypothyroidism.
centration is below the reference range, but other factors False-positive and false-negative serum TSH test results
(e.g., concurrent illness, questionable clinical signs, lack are common.
of hyperlipidemia) raise doubt about hypothyroidism (see Serum TSH should not be used, by itself, to diagnose
Diagnosis, p. 782). hypothyroidism.
Serum 3,5,3′-Triiodothyronine (T 3 )
Baseline Serum fT 4 Concentration This may be a component of canine thyroid panels.
Free T 4 , the non–protein-bound fraction of T 4 circulating in This is not the primary hormone secreted by the thyroid
blood, accounts for less than 1% of circulating T 4 . Currently, gland; T 3 is primarily produced from deiodination of
measurement of fT 4 is done by one of three methods: modi- fT 4 within cells of the body.
fied equilibrium dialysis, analog RIA, and analog chemilumi- T 3 is a poor gauge of thyroid gland function and should
nescent assay. Studies evaluating these assays for assessment not be used, by itself, to diagnose hypothyroidism.
of thyroid gland function in dogs and cats found comparable
sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy, suggesting that any one Serum Thyroglobulin (Tg) and Thyroid Hormone (T 3 and
T 4 ) Autoantibody Tests
of these three assays is acceptable for measuring fT 4 concen-
trations in dogs and cats. It is important that the assay used This is a common component of canine thyroid panels.
by the reference laboratory has been validated for use in dogs These are tests of thyroid gland pathology—not of thyroid
gland function.
and reference ranges established in dogs. In general, serum These tests are used to identify lymphocytic thyroiditis
fT 4 concentrations greater than 1.5 ng/dL (20 pmol/L) are and to explain unusual serum T 4 and T 3 test results.
consistent with euthyroidism, and values less than 0.8 ng/ They should never be used to diagnose hypothyroidism.
dL (10 pmol/L) especially less than 0.5 ng/dL (6 pmol/L)
are supportive of hypothyroidism, assuming the history and