Page 806 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 806
778 PART VI Endocrine Disorders
assay (Imulite Canine TSH), which has been shown to have 1.4
the highest precision compared with immunoradiometric 60
VetBooks.ir Unfortunately, all TSH assays have poor sensitivity for the 1.2
and enzyme immunometric assays (Marca et al., 2001).
diagnosis of hypothyroidism. In dogs with hypothyroidism,
20% to 40% have serum TSH concentrations in the reference
range. However, studies have shown that a high serum TSH
concentration has high specificity (>90%) for diagnosis of 1.0
hypothyroidism when serum T 4 and/or fT 4 is low in the same
serum sample. Proposed reasons for the poor sensitivity
include loss of TSH response by pituitary thyrotophs to low 0.8
serum T 4 concentrations over time, pulsatile TSH secretion 40
resulting in fluctuations in serum TSH concentration, sup- Serum TSH (ng/mL) Serum TSH (mU/L)
pression of the TSH response by concurrent illness or drugs, 0.6
and secondary hypothyroidism.
Most clinical laboratories use a serum TSH concentration
of 0.6 ng/mL as the upper limit of the reference range. The
lower limit of the reference range is currently below the 0.4
sensitivity of these assays; differentiation between low and 20
normal serum TSH concentrations is not possible.
Measurement of serum TSH concentration should be part 0.2
of the routine evaluation of thyroid gland function or may
be reserved for dogs with suspected hypothyroidism and
nondiagnostic serum T 4 test results. A serum TSH concen- 0 0
tration greater than 0.6 ng/mL in conjunction with a low Mild Moderate Severe
serum T 4 or fT 4 is consistent with hypothyroidism. Unfortu- (66) (95) (62)
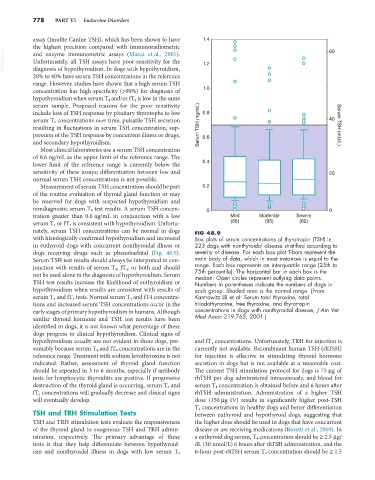
nately, serum TSH concentrations can be normal in dogs FIG 48.9
with histologically confirmed hypothyroidism and increased Box plots of serum concentrations of thyrotropin (TSH) in
in euthyroid dogs with concurrent nonthyroidal illness or 223 dogs with nonthyroidal disease stratified according to
dogs receiving drugs such as phenobarbital (Fig. 48.9). severity of disease. For each box plot T-bars represent the
Serum TSH test results should always be interpreted in con- main body of data, which in most instances is equal to the
junction with results of serum T 4 , fT 4 , or both and should range. Each box represents an interquartile range (25th to
not be used alone in the diagnosis of hypothyroidism. Serum 75th percentile). The horizontal bar in each box is the
median. Open circles represent outlying data points.
TSH test results increase the likelihood of euthyroidism or Numbers in parentheses indicate the numbers of dogs in
hypothyroidism when results are consistent with results of each group. Shaded area is the normal range. (From
serum T 4 and fT 4 tests. Normal serum T 4 and fT4 concentra- Kantrowitz LB et al: Serum total thyroxine, total
tions and increased serum TSH concentrations occur in the triiodothyronine, free thyroxine, and thyrotropin
early stages of primary hypothyroidism in humans. Although concentrations in dogs with nonthyroidal disease, J Am Vet
similar thyroid hormone and TSH test results have been Med Assoc 219:765, 2001.)
identified in dogs, it is not known what percentage of these
dogs progress to clinical hypothyroidism. Clinical signs of
hypothyroidism usually are not evident in these dogs, pre- and fT 4 concentrations. Unfortunately, TRH for injection is
sumably because serum T 4 and fT 4 concentrations are in the currently not available. Recombinant human TSH (rhTSH)
reference range. Treatment with sodium levothyroxine is not for injection is effective in stimulating thyroid hormone
indicated. Rather, assessment of thyroid gland function secretion in dogs but is not available at a reasonable cost.
should be repeated in 3 to 6 months, especially if antibody The current TSH stimulation protocol for dogs is 75 µg of
tests for lymphocytic thyroiditis are positive. If progressive rhTSH per dog administered intravenously, and blood for
destruction of the thyroid gland is occurring, serum T 4 and serum T 4 concentration is obtained before and 6 hours after
fT 4 concentrations will gradually decrease and clinical signs rhTSH administration. Administration of a higher TSH
will eventually develop. dose (150 µg IV) results in significantly higher post-TSH
T 4 concentrations in healthy dogs and better differentiation
TSH and TRH Stimulation Tests between euthyroid and hypothyroid dogs, suggesting that
TSH and TRH stimulation tests evaluate the responsiveness the higher dose should be used in dogs that have concurrent
of the thyroid gland to exogenous TSH and TRH admin- disease or are receiving medications (Boretti et al., 2009). In
istration, respectively. The primary advantage of these a euthyroid dog serum, T 4 concentration should be ≥ 2.5 µg/
tests is that they help differentiate between hypothyroid- dL (30 nmol/L) 6 hours after rhTSH administration, and the
ism and nonthyroidal illness in dogs with low serum T 4 6-hour post-rhTSH serum T 4 concentration should be ≥ 1.5