Page 850 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 850
822 PART VI Endocrine Disorders
Guardian BG Meter BG Sensor Sensor alarm Target range Hypo
VetBooks.ir 300
Glucose (mg/dL) 200 140
100
60
0 70
Fri 12:00AM 2:00AM 4:00AM 6:00AM 8:00AM 10:00AM 12:00PM 2:00PM 4:00PM 6:00PM 8:00PM 10:00PM Sat 12:00AM
5:30AM 12:00PM 5:00AM
261 (ICU) 200 (AT) 274 (ICU)
1.5 Detemir SC 1.5 Detemir SC
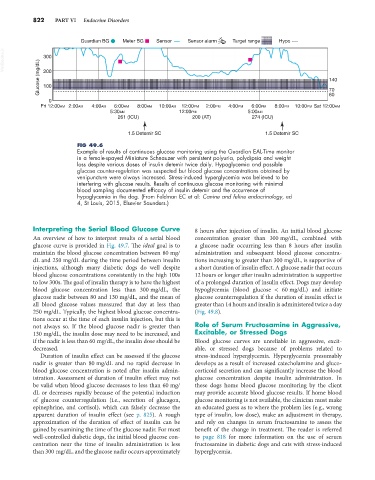
FIG 49.6
Example of results of continuous glucose monitoring using the Guardian EAL-Time monitor
in a female-spayed Miniature Schnauzer with persistent polyuria, polydipsia and weight
loss despite various doses of insulin detemir twice daily. Hypoglycemia and possible
glucose counter-regulation was suspected but blood glucose concentrations obtained by
venipuncture were always increased. Stress-induced hyperglycemia was believed to be
interfering with glucose results. Results of continuous glucose monitoring with minimal
blood sampling documented efficacy of insulin detemir and the occurrence of
hypoglycemia in the dog. (From Feldman EC et al: Canine and feline endocrinology, ed
4, St Louis, 2015, Elsevier Saunders.)
Interpreting the Serial Blood Glucose Curve 8 hours after injection of insulin. An initial blood glucose
An overview of how to interpret results of a serial blood concentration greater than 300 mg/dL, combined with
glucose curve is provided in Fig. 49.7. The ideal goal is to a glucose nadir occurring less than 8 hours after insulin
maintain the blood glucose concentration between 80 mg/ administration and subsequent blood glucose concentra-
dL and 250 mg/dL during the time period between insulin tions increasing to greater than 300 mg/dL, is supportive of
injections, although many diabetic dogs do well despite a short duration of insulin effect. A glucose nadir that occurs
blood glucose concentrations consistently in the high 100s 12 hours or longer after insulin administration is supportive
to low 300s. The goal of insulin therapy is to have the highest of a prolonged duration of insulin effect. Dogs may develop
blood glucose concentration less than 300 mg/dL, the hypoglycemia (blood glucose < 60 mg/dL) and initiate
glucose nadir between 80 and 130 mg/dL, and the mean of glucose counterregulation if the duration of insulin effect is
all blood glucose values measured that day at less than greater than 14 hours and insulin is administered twice a day
250 mg/dL. Typically, the highest blood glucose concentra- (Fig. 49.8).
tions occur at the time of each insulin injection, but this is
not always so. If the blood glucose nadir is greater than Role of Serum Fructosamine in Aggressive,
130 mg/dL, the insulin dose may need to be increased, and Excitable, or Stressed Dogs
if the nadir is less than 60 mg/dL, the insulin dose should be Blood glucose curves are unreliable in aggressive, excit-
decreased. able, or stressed dogs because of problems related to
Duration of insulin effect can be assessed if the glucose stress-induced hyperglycemia. Hyperglycemia presumably
nadir is greater than 80 mg/dL and no rapid decrease in develops as a result of increased catecholamine and gluco-
blood glucose concentration is noted after insulin admin- corticoid secretion and can significantly increase the blood
istration. Assessment of duration of insulin effect may not glucose concentration despite insulin administration. In
be valid when blood glucose decreases to less than 60 mg/ these dogs home blood glucose monitoring by the client
dL or decreases rapidly because of the potential induction may provide accurate blood glucose results. If home blood
of glucose counterregulation (i.e., secretion of glucagon, glucose monitoring is not available, the clinician must make
epinephrine, and cortisol), which can falsely decrease the an educated guess as to where the problem lies (e.g., wrong
apparent duration of insulin effect (see p. 825). A rough type of insulin, low dose), make an adjustment in therapy,
approximation of the duration of effect of insulin can be and rely on changes in serum fructosamine to assess the
gained by examining the time of the glucose nadir. For most benefit of the change in treatment. The reader is referred
well-controlled diabetic dogs, the initial blood glucose con- to page 818 for more information on the use of serum
centration near the time of insulin administration is less fructosamine in diabetic dogs and cats with stress-induced
than 300 mg/dL, and the glucose nadir occurs approximately hyperglycemia.