Page 851 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 851
CHAPTER 49 Disorders of the Endocrine Pancreas 823
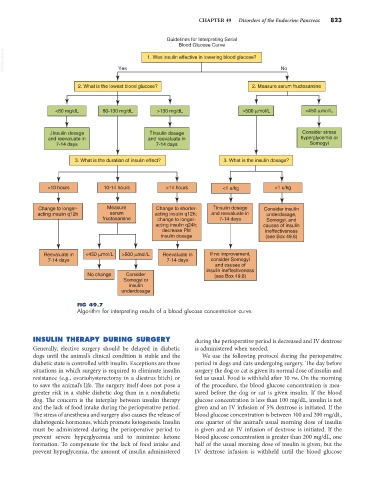
Guidelines for Interpreting Serial
Blood Glucose Curve
VetBooks.ir Yes 1. Was insulin effective in lowering blood glucose? No
2. What is the lowest blood glucose? 2. Measure serum fructosamine
<80 mg/dL 80-130 mg/dL >130 mg/dL >500 mol/L <450 mol/L
↓Insulin dosage ↑Insulin dosage Consider stress
and reevaluate in and reevaluate in hyperglycemia or
7-14 days 7-14 days Somogyi
3. What is the duration of insulin effect? 3. What is the insulin dosage?
<10 hours 10-14 hours >14 hours <1 u/kg >1 u/kg
Change to longer- Measure Change to shorter- ↑Insulin dosage Consider insulin
acting insulin q12h serum acting insulin q12h; and reevaluate in underdosage,
fructosamine change to longer- 7-14 days Somogyi, and
acting insulin q24h; causes of insulin
decrease PM ineffectiveness
insulin dosage (see Box 49.8)
Reevaluate in <450 mol/L >500 mol/L Reevaluate in If no improvement,
7-14 days 7-14 days consider Somogyi
and causes of
insulin ineffectiveness
No change Consider (see Box 49.8)
Somogyi or
insulin
underdosage
FIG 49.7
Algorithm for interpreting results of a blood glucose concentration curve.
INSULIN THERAPY DURING SURGERY during the perioperative period is decreased and IV dextrose
Generally, elective surgery should be delayed in diabetic is administered when needed.
dogs until the animal’s clinical condition is stable and the We use the following protocol during the perioperative
diabetic state is controlled with insulin. Exceptions are those period in dogs and cats undergoing surgery. The day before
situations in which surgery is required to eliminate insulin surgery the dog or cat is given its normal dose of insulin and
resistance (e.g., ovariohysterectomy in a diestrus bitch) or fed as usual. Food is withheld after 10 PM. On the morning
to save the animal’s life. The surgery itself does not pose a of the procedure, the blood glucose concentration is mea-
greater risk in a stable diabetic dog than in a nondiabetic sured before the dog or cat is given insulin. If the blood
dog. The concern is the interplay between insulin therapy glucose concentration is less than 100 mg/dL, insulin is not
and the lack of food intake during the perioperative period. given and an IV infusion of 5% dextrose is initiated. If the
The stress of anesthesia and surgery also causes the release of blood glucose concentration is between 100 and 200 mg/dL,
diabetogenic hormones, which promote ketogenesis. Insulin one quarter of the animal’s usual morning dose of insulin
must be administered during the perioperative period to is given and an IV infusion of dextrose is initiated. If the
prevent severe hyperglycemia and to minimize ketone blood glucose concentration is greater than 200 mg/dL, one
formation. To compensate for the lack of food intake and half of the usual morning dose of insulin is given, but the
prevent hypoglycemia, the amount of insulin administered IV dextrose infusion is withheld until the blood glucose