Page 43 - Rule Outs in Small Animal Medicine, Problem-oriented Assessment of Problems in Physical Examination and Clinical Pathology, 2nd Edition
P. 43
Internal Medicine Internal Medicine
Gastrointestinal tract Gastrointestinal tract
VetBooks.ir
Polyphagia
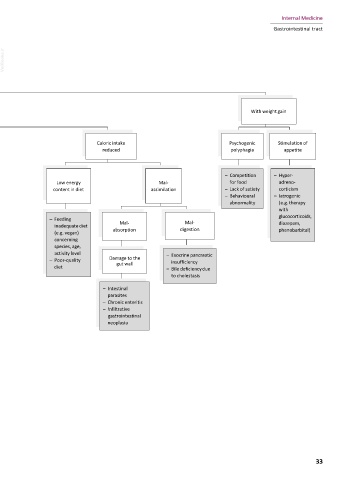
Without weight gain/ With weight gain
with weight loss
Increased calorie Loss of calories Caloric intake Psychogenic Stimulation of
requirements reduced polyphagia appetite
Energy needed for – Competition – Hyper-
additional Increased Gastro- Low energy Mal- for food adreno-
cells/tissue/ metabolism Renal intestinal content in diet assimilation – Lack of satiety corticism
organisms – Behavioural – Iatrogenic
abnormality (e.g. therapy
with
– Protein- – Protein- – Feeding glucocorticoids,
Parasite Physio- Mal- Mal- diazepam,
Pregnancy Neoplasia Hormonal losing losing inadequate diet
infestation logic absorption digestion phenobarbital)
nephrop- enter- (e.g. vegan)
athy opathy concerning
– Glucos- species, age,
– Gastro- Hyper- – Stress uria/ activity level Damage to the – Exocrine pancreatic
intestinal thyroidism – Lactation diabetes – Poor-quality gut wall insufficiency
parasites mellitus diet – Bile deficiency due
– Ecto- to cholestasis
parasites
– Diro- – Intestinal
filariosis parasites
– Chronic enteritis
– Infiltrative
gastrointestinal
neoplasia
32 33