Page 204 - Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 6th Edition
P. 204
CHAPTER 12 Cancer Chemotherapy 183
VetBooks.ir Survival Proliferation
Signal transduction Antimetabolites
inhibitors
G 1 Alkylating
Growth phase agents
Antimicrotubule Cross-linking
agents agents
Cell Topoisomerase
M inhibitors
Mitosis cycle
S
DNA replication
G 2
Growth phase
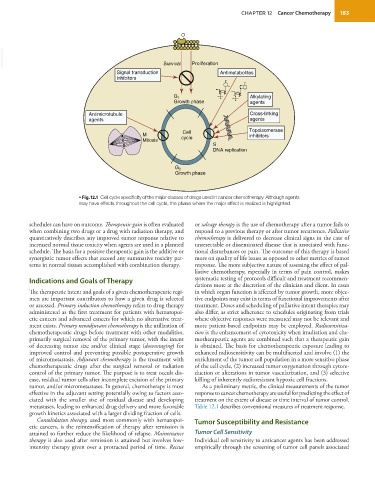
• Fig. 12.1 Cell cycle specificity of the major classes of drugs used in cancer chemotherapy. Although agents
may have effects throughout the cell cycle, the phase where the major effect is realized is highlighted.
schedules can have on outcome. Therapeutic gain is often evaluated or salvage therapy is the use of chemotherapy after a tumor fails to
when combining two drugs or a drug with radiation therapy, and respond to a previous therapy or after tumor recurrence. Palliative
quantitatively describes any improved tumor response relative to chemotherapy is delivered to decrease clinical signs in the case of
increased normal tissue toxicity when agents are used in a planned unresectable or disseminated disease that is associated with func-
schedule. The basis for a positive therapeutic gain is the additive or tional disturbances or pain. The outcome of this therapy is based
synergistic tumor effects that exceed any summative toxicity pat- more on quality of life issues as opposed to other metrics of tumor
terns in normal tissues accomplished with combination therapy. response. The more subjective nature of assessing the effect of pal-
liative chemotherapy, especially in terms of pain control, makes
Indications and Goals of Therapy systematic testing of protocols difficult and treatment recommen-
dations more at the discretion of the clinician and client. In cases
The therapeutic intent and goals of a given chemotherapeutic regi- in which organ function is affected by tumor growth, more objec-
men are important contributors to how a given drug is selected tive endpoints may exist in terms of functional improvements after
or assessed. Primary induction chemotherapy refers to drug therapy treatment. Doses and scheduling of palliative intent therapies may
administered as the first treatment for patients with hematopoi- also differ, as strict adherence to schedules originating from trials
etic cancers and advanced cancers for which no alternative treat- where objective responses were measured may not be relevant and
ment exists. Primary neoadjuvant chemotherapy is the utilization of more patient-based endpoints may be employed. Radiosensitiza-
chemotherapeutic drugs before treatment with other modalities, tion is the enhancement of cytotoxicity when irradiation and che-
primarily surgical removal of the primary tumor, with the intent motherapeutic agents are combined such that a therapeutic gain
of decreasing tumor size and/or clinical stage (downstaging) for is obtained. The basis for chemotherapeutic exposure leading to
improved control and preventing possible postoperative growth enhanced radiosensitivity can be multifaceted and involve (1) the
of micrometastasis. Adjuvant chemotherapy is the treatment with enrichment of the tumor cell population in a more sensitive phase
chemotherapeutic drugs after the surgical removal or radiation of the cell cycle, (2) increased tumor oxygenation through cytore-
control of the primary tumor. The purpose is to treat occult dis- duction or alterations in tumor vascularization, and (3) selective
ease, residual tumor cells after incomplete excision of the primary killing of inherently radioresistant hypoxic cell fractions.
tumor, and/or micrometastases. In general, chemotherapy is most As a preliminary metric, the clinical measurements of the tumor
effective in the adjuvant setting potentially owing to factors asso- response to cancer chemotherapy are useful for predicting the effect of
ciated with the smaller size of residual disease and developing treatment on the extent of disease or time interval of tumor control.
metastases, leading to enhanced drug delivery and more favorable Table 12.1 describes conventional measures of treatment response.
growth kinetics associated with a larger dividing fraction of cells.
Consolidation therapy, used most commonly with hematopoi- Tumor Susceptibility and Resistance
etic cancers, is the reintensification of therapy after remission is
attained to further reduce the likelihood of relapse. Maintenance Tumor Cell Sensitivity
therapy is also used after remission is attained but involves low- Individual cell sensitivity to anticancer agents has been addressed
intensity therapy given over a protracted period of time. Rescue empirically through the screening of tumor cell panels associated