Page 208 - Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 6th Edition
P. 208
CHAPTER 12 Cancer Chemotherapy 187
The AEs for anticancer agents may be categorized into acute
8 Too low toxicities (at the time or within 24–48 hours after treatment),
acute delayed effects (2–14 days), or cumulative/chronic toxic-
VetBooks.ir 6 ity (weeks, months, or years). Acute toxicity may include infu-
sion hypersensitivities because of histamine release associated
with allergic (l-asparaginase) or allergic-like (DOX) reactions, or
Neutrophils (× 1000) 4 Dose inc. side). Routine management of these events with antihistamines
vehicle-induced mast cell degranulation (e.g., paclitaxel, etopo-
and corticosteroids may significantly mitigate this problem. Acute
nausea and vomiting may occur with specific agents (e.g., cispla-
Just right
tin, dacarbazine, streptozotocin) or when the infusion is too rapid
2
(e.g., DOX). Preemptive antiemetic management often manages
Too high
these AEs. Drugs with vesicant properties can cause moderate or
severe tissue necrosis if not administered safely through a suitable
0 catheter. Vinca alkaloid, DOX, mechlorethamine, and actinomy-
0 10 20 30 40 50
cin D extravasations can be very severe situations that should be
Time (days) avoided, even if sedation is required or rescheduling is required
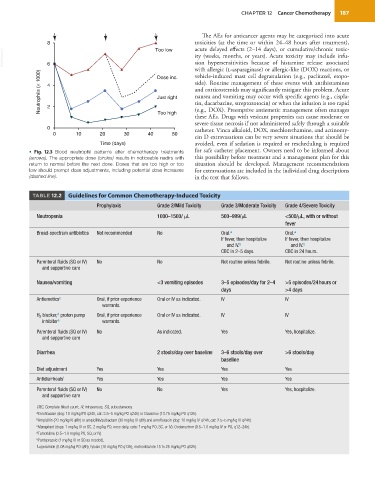
• Fig. 12.3 Blood neutrophil patterns after chemotherapy treatments for safe catheter placement. Owners need to be informed about
(arrows). The appropriate dose (circles) results in noticeable nadirs with this possibility before treatment and a management plan for this
return to normal before the next dose. Doses that are too high or too situation should be developed. Management recommendations
low should prompt dose adjustments, including potential dose increases for extravasations are included in the individual drug descriptions
(dashed line). in the text that follows.
TABLE 12.2 Guidelines for Common Chemotherapy-Induced Toxicity
Prophylaxis Grade 2/Mild Toxicity Grade 3/Moderate Toxicity Grade 4/Severe Toxicity
Neutropenia 1000–1500/ μL 500–999/μL <500/μL, with or without
fever
Broad-spectrum antibiotics Not recommended No Oral. a Oral. a
If fever, then hospitalize If fever, then hospitalize
and IV. b and IV. b
CBC in 2–5 days. CBC in 24 hours.
Parenteral fluids (SQ or IV) No No Not routine unless febrile. Not routine unless febrile.
and supportive care
Nausea/vomiting <3 vomiting episodes 3–5 episodes/day for 2–4 >5 episodes/24 hours or
days >4 days
Antiemetics c Oral, if prior experience Oral or IV as indicated. IV IV
warrants.
d
H 2 blocker, proton pump Oral, if prior experience Oral or IV as indicated. IV IV
inhibitor e warrants.
Parenteral fluids (SQ or IV) No As indicated. Yes Yes, hospitalize.
and supportive care
Diarrhea 2 stools/day over baseline 3–6 stools/day over >6 stools/day
baseline
Diet adjustment Yes Yes Yes Yes
Antidiarrheals f Yes Yes Yes Yes
Parenteral fluids (SQ or IV) No No Yes Yes, hospitalize.
and supportive care
CBC, Complete blood count; IV, intravenous; SQ, subcutaneous.
a Enrofloxacin (dog: 10 mg/kg PO q24h, cat: 2.5–5 mg/kg PO q24h) or Clavamox (13.75 mg/kg PO q12h).
b Ampicillin (20 mg/kg IV q8h) or ampicillin/sulbactam (30 mg/kg IV q8h) and enrofloxacin (dog: 10 mg/kg IV q24h, cat: 2.5–5 mg/kg IV q24h).
c Maropitant (dogs: 1 mg/kg IV or SC, 2 mg/kg PO, once daily, cats: 1 mg/kg PO, SC, or IV). Ondansetron (0.5–1.0 mg/kg IV or PO, q12–24h).
d Famotidine (0.5–1.0 mg/kg PO, SQ, or IV).
e Pantoprazole (1 mg/kg IV or SQ as needed).
f Loperamide (0.08 mg/kg PO q8h); tylosin (10 mg/kg PO q12h); metronidazole 15 to 25 mg/kg PO q12h).