Page 211 - Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 6th Edition
P. 211
190 PART 3 Therapeutic Modalities for the Cancer Patient
1.0 antineoplastic activity. 105–107 Mechlorethamine undergoes spon-
taneous hydrolysis to 2-hydroxyethyl-2-chloroethylmethylamine
and bis-2-hydroxyethylmethylamine, yielding nucleophilic reac-
VetBooks.ir 0.8 tive centers capable of forming DNA cross-links. 108
Clinical Pharmacology. Mechlorethamine rapidly disappears
Proportion 0.6 from the plasma after administration, primarily through spon-
taneous degradation, although some percentage of the drug is
Mechlorethamine uptake into cells
109
enzymatically metabolized.
0.4
seems to be carrier mediated, with decreased uptake as a mecha-
nism for resistance. 110
0.2 p-value 0.009
Experience with mechlorethamine as a single agent is not
reported, although gastrointestinal (GI) and bone marrow tox-
0.0 icities are dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) of conventional mech-
0 1 2 3 4 lorethamine-containing protocols. This drug is a strong vesicant
Years and can cause severe tissue necrosis if extravasated. In case of
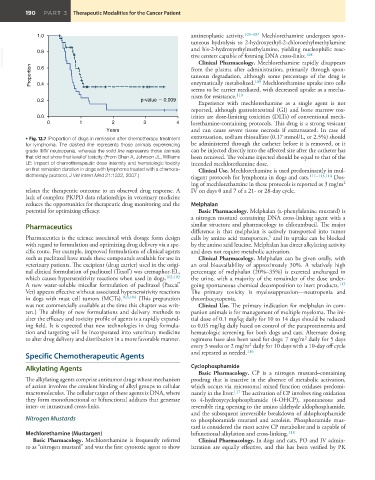
• Fig. 12.7 Proportion of dogs in remission after chemotherapy treatment extravasation, sodium thiosulfate (0.17 mmol/L, or 2.5%) should
for lymphoma. The dashed line represents those animals experiencing be administered through the catheter before it is removed, or it
grade III/IV neutropenia, whereas the solid line represents those animals can be injected directly into the affected site after the catheter has
that did not show that level of toxicity. (From Ghan A, Johnson JL, Williams been removed. The volume injected should be equal to that of the
LE: Impact of chemotherapeutic dose intensity and hematologic toxicity intended mechlorethamine dose.
on first remission duration in dogs with lymphoma treated with a chemora- Clinical Use. Mechlorethamine is used predominantly in mul-
diotherapy protocol, J Vet Intern Med 21:1332, 2007.) tiagent protocols for lymphoma in dogs and cats. 111–113,114 Dos-
ing of mechlorethamine in these protocols is reported as 3 mg/m
2
relates the therapeutic outcome to an observed drug response. A IV on days 0 and 7 of a 21- or 28-day cycle.
lack of complete PK/PD data relationships in veterinary medicine
reduces the opportunities for therapeutic drug monitoring and the Melphalan
potential for optimizing efficacy. Basic Pharmacology. Melphalan (l-phenylalanine mustard) is
a nitrogen mustard containing DNA cross-linking agent with a
Pharmaceutics similar structure and pharmacology to chlorambucil. The major
difference is that melphalan is actively transported into tumor
5
Pharmaceutics is the science associated with dosage form design cells by amino acid transporters, and its uptake can be blocked
with regard to formulation and optimizing drug delivery via a spe- by the amino acid leucine. Melphalan has direct alkylating activity
cific route. For example, improved formulations of clinical agents and does not require metabolic activation.
such as paclitaxel have made these compounds available for use in Clinical Pharmacology. Melphalan can be given orally, with
veterinary patients. The excipient (drug carrier) used in the origi- an oral bioavailability of approximately 30%. A relatively high
®
nal clinical formulation of paclitaxel (Taxol ) was cremaphor-EL, percentage of melphalan (20%–35%) is excreted unchanged in
which causes hypersensitivity reactions when used in dogs. 102,103 the urine, with a majority of the remainder of the dose under-
A new water-soluble micellar formulation of paclitaxel (Paccal ® going spontaneous chemical decomposition to inert products. 115
Vet) appears effective without associated hypersensitivity reactions The primary toxicity is myelosuppression—neutropenia and
in dogs with mast cell tumors (MCTs). 103,104 (This preparation thrombocytopenia.
was not commercially available at the time this chapter was writ- Clinical Use. The primary indication for melphalan in com-
ten.) The ability of new formulations and delivery methods to panion animals is for management of multiple myeloma. The ini-
alter the efficacy and toxicity profile of agents is a rapidly expand- tial dose of 0.1 mg/kg daily for 10 to 14 days should be reduced
ing field. It is expected that new technologies in drug formula- to 0.05 mg/kg daily based on control of the paraproteinemia and
tion and targeting will be incorporated into veterinary medicine hematologic screening for both dogs and cats. Alternate dosing
2
to alter drug delivery and distribution in a more favorable manner. regimens have also been used for dogs: 7 mg/m daily for 5 days
2
every 3 weeks or 2 mg/m daily for 10 days with a 10-day off cycle
Specific Chemotherapeutic Agents and repeated as needed. 116
Alkylating Agents Cyclophosphamide
Basic Pharmacology. CP is a nitrogen mustard–containing
The alkylating agents comprise antitumor drugs whose mechanism prodrug that is inactive in the absence of metabolic activation,
of action involves the covalent binding of alkyl groups to cellular which occurs via microsomal mixed function oxidases predomi-
macromolecules. The cellular target of these agents is DNA, where nantly in the liver. 117 The activation of CP involves ring oxidation
they form monofunctional or bifunctional adducts that generate to 4-hydroxycyclophosphamide (4-OHCP), spontaneous and
inter- or intrastrand cross-links. reversible ring opening to the amino aldehyde aldophosphamide,
and the subsequent irreversible breakdown of aldophosphamide
Nitrogen Mustards to phosphoramide mustard and acrolein. Phosphoramide mus-
tard is considered the most active CP metabolite and is capable of
Mechlorethamine (Mustargen) bifunctional alkylation and cross-linking. 118
Basic Pharmacology. Mechlorethamine is frequently referred Clinical Pharmacology. In dogs and cats, PO and IV admin-
to as “nitrogen mustard” and was the first cytotoxic agent to show istration are equally effective, and this has been verified by PK