Page 522 - Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 6th Edition
P. 522
500 PART IV Specific Malignancies in the Small Animal Patient
resulted in radiation-related deaths in one-third of evaluated type. RT-related morbidity can be significantly reduced in dogs
dogs. 127 A recent investigation of a similar approach evalu- with sinonasal tumors when IMRT is used. 122,138 A clinical study
compared radiation-induced ocular toxicity in dogs with nasal
ated a simultaneously integrated boost using highly conformal
VetBooks.ir intensity-modulated RT and led to clinically acceptable side tumors treated with IMRT to that of historical controls treated
effects in a small pilot study of nine dogs in which a 20% dose
IMRT reduced the radiation dose
with conventional 2D RT.
122
increase was delivered to gross disease. 134 These preliminary delivered to the eyes and resulted in bilateral ocular sparing.
results suggest that modern conformal techniques may make This was in contrast to profound ocular morbidity observed in
dose escalation a feasible treatment strategy. Further evaluation the historical control group. MSTs for both groups were similar.
is needed to confirm these findings and to assess effectiveness Paramount to the success of highly conformal RT is precise daily
with respect to tumor control. patient positioning. 137 Millimeter variation in patient setup can
3. The use of radiosensitizers in conjunction with ionizing result in underdosing of the tumor and unintended irradiation
radiation has been reported. A Veterinary Radiation Therapy of normal tissues. Daily setup inaccuracies associated with con-
Oncology Group (VRTOG) pilot study described the use of ventional (nonrigid) immobilization techniques used in veteri-
gemcitabine as a radiosensitizer for sinonasal carcinoma. 135 nary RT reduce precision of IMRT delivery over a multiple-week
2
Gemcitabine was given intravenously at a dosage of 50 mg/m course of treatment for nasal tumors. 140 Daily image guidance is
twice weekly before daily RT. The authors reported significant often necessary to ensure daily setup precision. 140 This is referred
hematologic toxicity (neutropenia) and local acute tissue com- to as image-guided IMRT (IGRT). Rigid immobilization tech-
plications associated with this dose and schedule. In another niques (head and cranial body fixation devices) have been devel-
report, low-dose cisplatin (7.5 mg/m given intravenously every oped for veterinary patients, 141–144,145 and, in conjunction with
2
other day) administered in conjunction with definitive RT was daily “on-board” image guidance, permit successful implementa-
well tolerated and did not appear to cause an increase in acute tion of highly conformal therapy. 140,141,145,146 Also critical to the
or late radiation effects. 123 The efficacy of this approach with success of IMRT is the accuracy of radiation target and normal
respect to improvement of clinical outcome is not known. A tissue delineation in the treatment planning process, as well as the
combination of RT and cisplatin, administered intramuscu- choice of dose calculation algorithm in the treatment planning
larly throughout therapy using a slow-release polymer system system. 147–149
(open cell polylactic acid polymer impregnated with platinum A newly emerging application of IMRT/IGRT is stereotac-
[OPLA-Pt]), was well tolerated; however, survival times were tic RT (SRT). SRT refers to the delivery of high-dose (ablative)
similar to those in other studies that used RT alone (MST: radiation in a single dose or a few fractions. 150 The treatment is
474 days). 120 Use of firocoxib, a COX-2 inhibitor, was evalu- delivered with extreme accuracy, and the dose is pinpointed to the
ated in combination with RT in a small, underpowered study. tumor, minimizing the effect on nearby organs. The high degree
Quality of life was improved in the dogs receiving the nonste- of precision and sharp dose fall-off at the edge of the tumor target
roidal antiinflammatory drug, but there was no difference in is achieved by delivering many (up to hundreds) irregular sub-
progression-free interval or overall survival compared with RT fields. This is done using specialized software and sophisticated
alone. 136 multileaf collimation to create a complex intensity pattern. 150 To
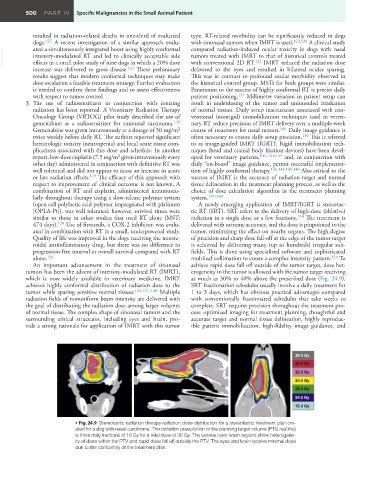
An important advancement in the treatment of sinonasal achieve rapid dose fall off outside of the tumor target, dose het-
tumors has been the advent of intensity-modulated RT (IMRT), erogeneity in the tumor is allowed with the tumor target receiving
which is now widely available in veterinary medicine. IMRT as much as 30% to 40% above the prescribed dose (Fig. 24.9).
achieves highly conformal distribution of radiation dose to the SRT fractionation schedules usually involve a daily treatment for
tumor while sparing sensitive normal tissues. 122,137–140 Multiple 1 to 3 days, which has obvious practical advantages compared
radiation fields of nonuniform beam intensity are delivered with with conventionally fractionated schedules that take weeks to
the goal of distributing the radiation dose among larger volumes complete. SRT requires precision throughout the treatment pro-
of normal tissue. The complex shape of sinonasal tumors and the cess: optimized imaging for treatment planning, thoughtful and
surrounding critical structures, including eyes and brain, pro- accurate target and normal tissue delineation, highly reproduc-
vide a strong rationale for application of IMRT with this tumor ible patient immobilization, high-fidelity image guidance, and
36.0 Gy
33.0 Gy
32.0 Gy
30.0 Gy
28.5 Gy
24.0 Gy
15.0 Gy
• Fig. 24.9 Stereotactic radiation therapy radiation dose distribution for a stereotactic treatment plan cre-
ated for a dog with nasal carcinoma. The radiation prescription to the planning target volume (PTV, red line)
is three daily fractions of 10 Gy for a total dose of 30 Gy. The various color wash regions show heterogene-
ity of dose within the PTV and rapid dose fall off outside the PTV. The eyes and brain receive minimal dose
due to the conformity of the treatment plan.