Page 94 - Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 6th Edition
P. 94
CHAPTER 3 The Pathology of Neoplasia 73
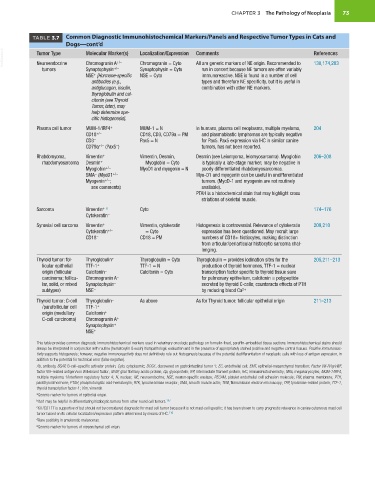
TABLE 3.7 Common Diagnostic Immunohistochemical Markers/Panels and Respective Tumor Types in Cats and
Dogs—cont’d
VetBooks.ir Tumor Type Molecular Marker(s) Localization/Expression Comments References
+/–
Chromogranin = Cyto
All are generic markers of NE origin. Recommended to
Chromogranin A
138,174,203
Neuroendocrine
tumors Synaptophysin +/– Synaptophysin = Cyto run in concert because NE tumors are often variably
+
NSE [Hormone-specific NSE = Cyto immunoreactive. NSE is found in a number of cell
antibodies (e.g., types and therefore NE specificity, but it is useful in
antiglucagon, insulin, combination with other NE markers.
thyroglobulin and cal-
citonin (see Thyroid
Tumor, later), may
help determine spe-
cific histogenesis].
Plasma cell tumor MUM-1/IRF4 + MUM-1 = N In humans, plasma cell neoplasms, multiple myeloma, 204
CD18 +/− CD18, CD3, CD79a = PM and plasmablastic lymphomas are typically negative
CD3 − Pax5 = N for Pax5. Pax5 expression via IHC in similar canine
CD79a +/− (Pax5 ) tumors, has not been reported.
−
Rhabdomyoma, Vimentin + Vimentin, Desmin, Desmin (see Leiomyoma, leiomyosarcoma). Myoglobin 206–208
rhabdomyosarcoma Desmin + Myoglobin = Cyto is typically a late-stage marker; may be negative in
Myoglobin +/− MyoD1 and myogenin = N poorly differentiated rhabdomyosarcomas.
−
SMA (MyoD1 +/− Myo-D1 and myogenin can be useful in undifferentiated
Myogenin +/− ; tumors. (MyoD-1 and myogenin are not routinely
see comments) available).
PTAH is a histochemical stain that may highlight cross
striations of skeletal muscle.
+ e
Sarcoma Vimentin Cyto 174–176
Cytokeratin −
Synovial cell sarcoma Vimentin + Vimentin, cytokeratin Histogenesis is controversial. Relevance of cytokeratin 209,210
Cytokeratin +/– = Cyto expression has been questioned. May recruit large
CD18 – CD18 = PM numbers of CD18+ histiocytes, making distinction
from articular/periarticular histiocytic sarcoma chal-
lenging.
Thyroid tumor: fol- Thyroglobulin + Thyroglobulin = Cyto Thyroglobulin = provides iodination sites for the 205,211–213
licular epithelial TTF-1 + TTF-1 = N production of thyroid hormones, TTF-1 = nuclear
origin (follicular Calcitonin − Calcitonin = Cyto transcription factor specific to thyroid tissue save
carcinoma; follicu- Chromogranin A − for pulmonary epithelium, calcitonin = polypeptide
lar, solid, or mixed Synaptophysin − secreted by thyroid C-cells; counteracts effects of PTH
subtypes) NSE − by reducing blood Ca 2+
Thyroid tumor: C-cell Thyroglobulin − As above As for Thyroid tumor: follicular epithelial origin 211–213
/parafollicular cell TTF-1 +
origin (medullary Calcitonin +
C-cell carcinoma) Chromogranin A +
Synaptophysin +
NSE +
This table provides common diagnostic immunohistochemical markers used in veterinary oncologic pathology on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections. Immunohistochemical stains should
always be interpreted in conjunction with routine (hematoxylin & eosin) histopathologic evaluation and in the presence of appropriately stained positive and negative control tissues. Positive immunoreac-
tivity supports histogenesis; however, negative immunoreactivity does not definitively rule out histogenesis because of the potential dedifferentiation of neoplastic cells with loss of antigen expression, in
addition to the potential for technical error (false negative).
Ab, antibody, BSAP, B-cell–specific activator protein; Cyto, cytoplasmic; DOG1, discovered on gastrointestinal tumor 1; EC, endothelial cell; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; Factor VIII-RAg/vWF,
factor VIII–related antigen/von Willebrand factor; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; Gp, glycoprotein; IFP, intermediate filament protein; IHC, immunohistochemistry; MKs, megakaryocytes; MUM-1/IRF4,
multiple myeloma 1/interferon regulatory factor 4; N, nuclear; NE, neuroendocrine; NSE, neuron-specific enolase; PECAM, platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule; PM, plasma membrane; PTH,
parathyroid hormone; PTAH, phosphotungstic acid-hematoxylin; RTK, tyrosine kinase receptor; SMA, smooth muscle actin; TEM, Transmission electron microscopy; TRP, tyrosinase-related protein; TTF-1,
thyroid transcription factor-1; Vim, vimentin.
a Generic marker for tumors of epithelial origin.
b Iba1 may be helpful in differentiating histiocytic tumors from other round cell tumors. 187
c KIT/CD117 is supportive of but should not be considered diagnostic for mast cell tumor because it is not mast-cell specific; it has been shown to carry prognostic relevance in canine cutaneous mast cell
tumor based on its cellular localization/expression pattern determined by means of IHC. 116
d Rare positivity in amelanotic melanomas.
e Generic marker for tumors of mesenchymal cell origin.