Page 177 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 177
162 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
(A) (B)
VetBooks.ir a Palmar I.
Suspensory I.
Cruciate sesamoidean I.
e e a Palmar annular I.
e
Extensor slip of
suspensory I.
Oblique sesamoidean I.
b
b
Straight sesamoidean I. Digital flexor tendons
c
f c
f
d
d
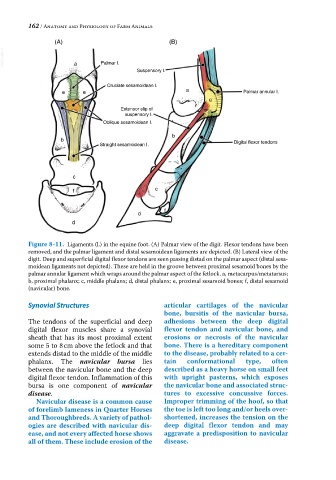
Figure 8-11. Ligaments (l.) in the equine foot. (A) Palmar view of the digit. Flexor tendons have been
removed, and the palmar ligament and distal sesamoidean ligaments are depicted. (B) Lateral view of the
digit. Deep and superficial digital flexor tendons are seen passing distad on the palmar aspect (distal sesa-
moidean ligaments not depicted). These are held in the groove between proximal sesamoid bones by the
palmar annular ligament which wraps around the palmar aspect of the fetlock. a, metacarpus/metatarsus;
b, proximal phalanx; c, middle phalanx; d, distal phalanx; e, proximal sesamoid bones; f, distal sesamoid
(navicular) bone.
Synovial Structures articular cartilages of the navicular
bone, bursitis of the navicular bursa,
The tendons of the superficial and deep adhesions between the deep digital
digital flexor muscles share a synovial flexor tendon and navicular bone, and
sheath that has its most proximal extent erosions or necrosis of the navicular
some 5 to 8 cm above the fetlock and that bone. There is a hereditary component
extends distad to the middle of the middle to the disease, probably related to a cer-
phalanx. The navicular bursa lies tain conformational type, often
between the navicular bone and the deep described as a heavy horse on small feet
digital flexor tendon. Inflammation of this with upright pasterns, which exposes
bursa is one component of navicular the navicular bone and associated struc-
disease. tures to excessive concussive forces.
Navicular disease is a common cause Improper trimming of the hoof, so that
of forelimb lameness in Quarter Horses the toe is left too long and/or heels over-
and Thoroughbreds. A variety of pathol- shortened, increases the tension on the
ogies are described with navicular dis- deep digital flexor tendon and may
ease, and not every affected horse shows aggravate a predisposition to navicular
all of them. These include erosion of the disease.